Volcanism In Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The 2,677‑million-year-old
The 2,677‑million-year-old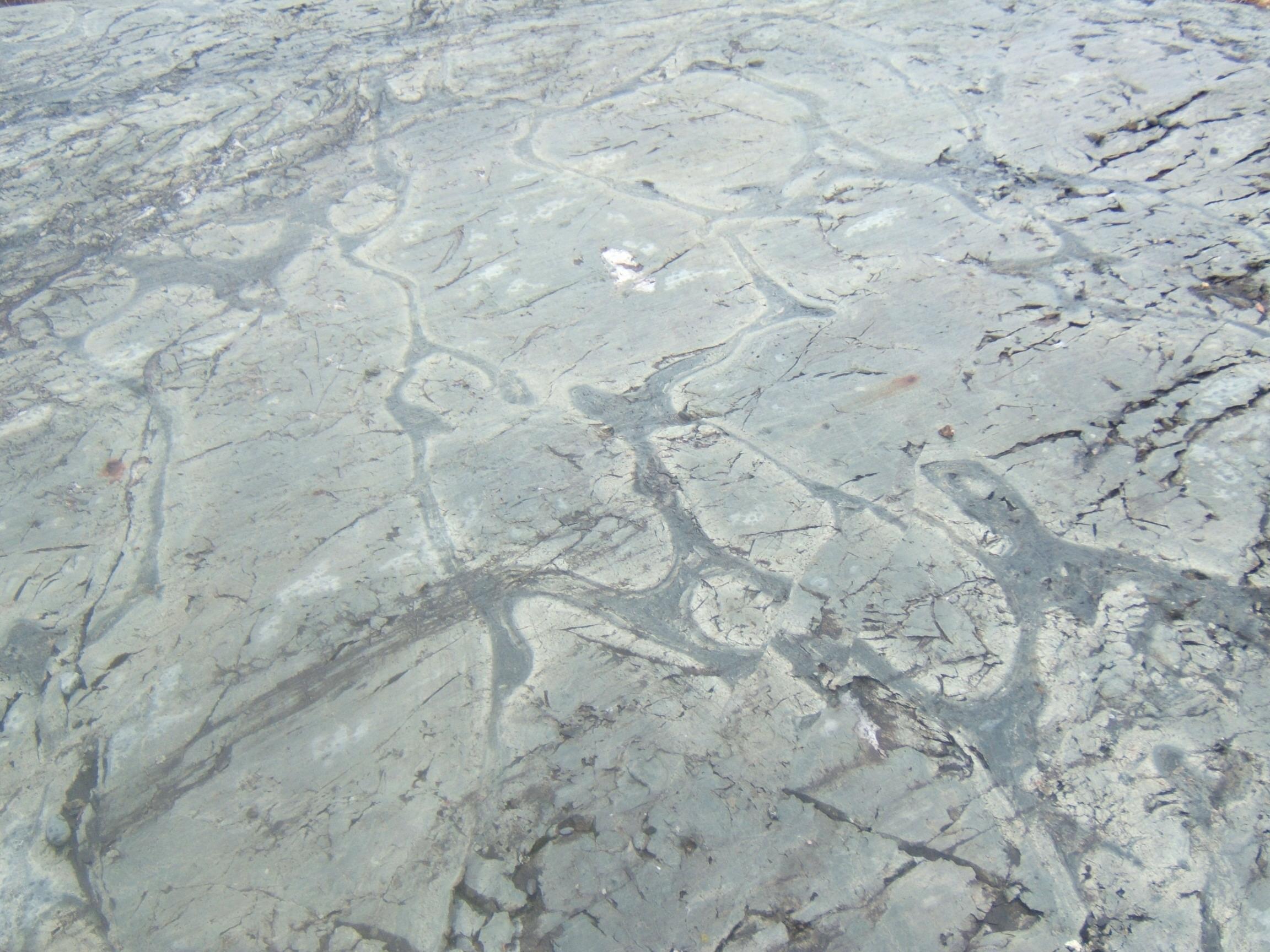  The 1884- to 1870‑million-year-old
The 1884- to 1870‑million-year-old  During the
During the  Periods of volcanic activity occurred throughout central Canada during the
Periods of volcanic activity occurred throughout central Canada during the  The
The
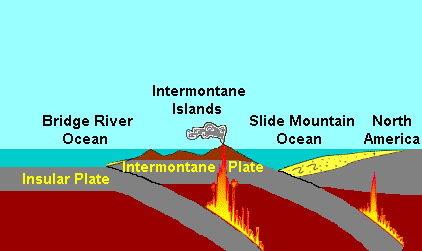 The Canadian portion of the
The Canadian portion of the  After the sedimentary and igneous rocks were folded and crushed, it resulted in the creation of a new continental shelf and coastline. The Insular Plate continued to subduct under the new continental shelf and coastline about 130 million years ago during the mid
After the sedimentary and igneous rocks were folded and crushed, it resulted in the creation of a new continental shelf and coastline. The Insular Plate continued to subduct under the new continental shelf and coastline about 130 million years ago during the mid  The Farallon Plate continued to subduct under the new continental margin of Western Canada after the Insular Plate and Insular Islands collided with the former continental margin, supporting a new chain of volcanoes on the mainland of Western Canada called the
The Farallon Plate continued to subduct under the new continental margin of Western Canada after the Insular Plate and Insular Islands collided with the former continental margin, supporting a new chain of volcanoes on the mainland of Western Canada called the  One of the major aspects that changed early during the Coast Range Arc was the status of the northern end of the Farallon Plate, a portion now known as the
One of the major aspects that changed early during the Coast Range Arc was the status of the northern end of the Farallon Plate, a portion now known as the
 As the last of the Kula Plate decayed and the Farallon Plate advanced back into this area from the south, it once again started to subduct under the continental margin of Western Canada 37 million years ago, supporting a chain of volcanoes called the
As the last of the Kula Plate decayed and the Farallon Plate advanced back into this area from the south, it once again started to subduct under the continental margin of Western Canada 37 million years ago, supporting a chain of volcanoes called the 
 The four-million-year-old Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, a north-south trending zone of volcanoes and volcanic rock in the southern
The four-million-year-old Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, a north-south trending zone of volcanoes and volcanic rock in the southern  The Chilcotin Group, a large igneous province and volcanic plateau in south-central British Columbia, consists of thin, flat-lying, poorly formed columnar basalt lava flows that have formed as a result of partial melting in a weak zone in the upper part of the Earth's mantle (geology), mantle within a
The Chilcotin Group, a large igneous province and volcanic plateau in south-central British Columbia, consists of thin, flat-lying, poorly formed columnar basalt lava flows that have formed as a result of partial melting in a weak zone in the upper part of the Earth's mantle (geology), mantle within a
 The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northwestern British Columbia, also called the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is the most active volcanic region in Canada. It comprises a large number of small cinder cones and associated lava plains, and three large, compositionally diverse volcanoes, known as the Level Mountain, the Mount Edziza volcanic complex, and Hoodoo Mountain. In the south the volcanic province is somewhat narrow and crosses diagonally through the northwesterly structural trend of the Coast Mountains. Farther north it is less clearly defined, forming a large arch that swings westward through central Yukon. Volcanoes within the British Columbia portion of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are disposed along short, northerly trending en-echelon segments which, in the British Columbia portion of the volcanic province, are unmistakably involved with north-trending rift structures including synvolcanic grabens and half-grabens similar to the East African Rift, which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward across eastern Africa. The Northern Cordilleran rift system formed as a result of the North American continent being stretched by extensional forces as the Pacific Plate slides northward along the Queen Charlotte Fault to the west, on its way to the Aleutian Trench, which extends along the southern coastline of Alaska and the adjacent waters of northeastern Siberia off the coast of Kamchatka Peninsula. As the continental crust stretches, the near-surface rocks fracture along steeply dipping cracks parallel to the rift known as fault (geology), faults. Hot basaltic magma rises along these fractures to create passive lava eruptions. The compositions of lavas in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are mantle-derived alkali olivine basalt, lesser hawaiite and basanite, which form the large shield volcanoes and small cinder cones throughout the volcanic province. Many of them contain inclusions of lherzolite. The large central volcanoes of the volcanic province consist largely of trachyte, pantellerite, and comendite lavas. These lava compositions were formed by fractionation of primary alkali basalt magma in crustal reservoirs. A region of continental rifting, such as the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, would support the development of high-level reservoirs of sufficient size and thermal capacity to sustain prolonged fractionation.
The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northwestern British Columbia, also called the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is the most active volcanic region in Canada. It comprises a large number of small cinder cones and associated lava plains, and three large, compositionally diverse volcanoes, known as the Level Mountain, the Mount Edziza volcanic complex, and Hoodoo Mountain. In the south the volcanic province is somewhat narrow and crosses diagonally through the northwesterly structural trend of the Coast Mountains. Farther north it is less clearly defined, forming a large arch that swings westward through central Yukon. Volcanoes within the British Columbia portion of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are disposed along short, northerly trending en-echelon segments which, in the British Columbia portion of the volcanic province, are unmistakably involved with north-trending rift structures including synvolcanic grabens and half-grabens similar to the East African Rift, which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward across eastern Africa. The Northern Cordilleran rift system formed as a result of the North American continent being stretched by extensional forces as the Pacific Plate slides northward along the Queen Charlotte Fault to the west, on its way to the Aleutian Trench, which extends along the southern coastline of Alaska and the adjacent waters of northeastern Siberia off the coast of Kamchatka Peninsula. As the continental crust stretches, the near-surface rocks fracture along steeply dipping cracks parallel to the rift known as fault (geology), faults. Hot basaltic magma rises along these fractures to create passive lava eruptions. The compositions of lavas in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are mantle-derived alkali olivine basalt, lesser hawaiite and basanite, which form the large shield volcanoes and small cinder cones throughout the volcanic province. Many of them contain inclusions of lherzolite. The large central volcanoes of the volcanic province consist largely of trachyte, pantellerite, and comendite lavas. These lava compositions were formed by fractionation of primary alkali basalt magma in crustal reservoirs. A region of continental rifting, such as the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, would support the development of high-level reservoirs of sufficient size and thermal capacity to sustain prolonged fractionation.
 The Anahim Volcanic Belt extends from coastal British Columbia across the Coast Mountains into the Interior Plateau. Its western end is defined by alkaline intrusive and comagmatic volcanic rocks of the Bella Bella-King Island complex, exposed in fjords and islands of the western Coast Mountains. The central portion of the Anahim Volcanic Belt contains three complex shield volcanoes, known as the Rainbow Range (Coast Mountains), Rainbow, Ilgachuz Range, Ilgachuz, and Itcha Range, Itcha ranges. These fairly dissected shield volcanoes lie on the northern end of the Chilcotin Group lava plateau and distal lava flows at the margins of the shield volcanoes merge imperceptibly with flat-lying lava flows comprising the Chilcotin Group lava plateau. Unlike the Chilcotin Group basalt, which is not associated with any felsic derivatives, the volcanoes of the central Anahim Volcanic Belt are markedly bimodal, comprising a mixed assemblage of basalt and peralkaline silicic rocks. While volcanoes of the Anahim Volcanic Belt appear to merge laterally with the Chilcotin Group lavas, the particular nature and connection between the Anahim Volcanic Belt and the Chilcotin Group is unknown. However, volcanoes within the Anahim Volcanic Belt usually become younger from coastal British Columbia to near the small city of Quesnel, British Columbia, Quesnel further east, indicating these volcanoes may have formed as a result of the North American Plate passing over a possible mantle plume known as the Anahim hotspot, whereas the Chilcotin Group is related to back-arc basin volcanism. Nazko Cone, a cluster of basaltic cinder cones in the Nazko, British Columbia, Nazko area west of Quesnel forms the youngest and most easterly part of the Anahim Volcanic Belt with dates of 7,200 years.
The Anahim Volcanic Belt extends from coastal British Columbia across the Coast Mountains into the Interior Plateau. Its western end is defined by alkaline intrusive and comagmatic volcanic rocks of the Bella Bella-King Island complex, exposed in fjords and islands of the western Coast Mountains. The central portion of the Anahim Volcanic Belt contains three complex shield volcanoes, known as the Rainbow Range (Coast Mountains), Rainbow, Ilgachuz Range, Ilgachuz, and Itcha Range, Itcha ranges. These fairly dissected shield volcanoes lie on the northern end of the Chilcotin Group lava plateau and distal lava flows at the margins of the shield volcanoes merge imperceptibly with flat-lying lava flows comprising the Chilcotin Group lava plateau. Unlike the Chilcotin Group basalt, which is not associated with any felsic derivatives, the volcanoes of the central Anahim Volcanic Belt are markedly bimodal, comprising a mixed assemblage of basalt and peralkaline silicic rocks. While volcanoes of the Anahim Volcanic Belt appear to merge laterally with the Chilcotin Group lavas, the particular nature and connection between the Anahim Volcanic Belt and the Chilcotin Group is unknown. However, volcanoes within the Anahim Volcanic Belt usually become younger from coastal British Columbia to near the small city of Quesnel, British Columbia, Quesnel further east, indicating these volcanoes may have formed as a result of the North American Plate passing over a possible mantle plume known as the Anahim hotspot, whereas the Chilcotin Group is related to back-arc basin volcanism. Nazko Cone, a cluster of basaltic cinder cones in the Nazko, British Columbia, Nazko area west of Quesnel forms the youngest and most easterly part of the Anahim Volcanic Belt with dates of 7,200 years.
 The Explorer Ridge, an mid-ocean ridge, underwater mountain range lying west of Vancouver Island on the Coast of British Columbia, consists of a north-south trending rift zone. It contains one major segment known as the Southern Explorer Ridge, along with other smaller segments, such as the Northern Explorer Ridge. With a depth of , the Southern Explorer Ridge is relatively shallow in comparison with most other rift zones of the northeast Pacific Ocean, indicating there has been considerable volcanic activity along this part of the Explorer Ridge in the past 100,000 years. Magic Mountain (hydrothermal field), Magic Mountain, a large hydrothermal vent area on the Southern Explorer Ridge, is a scene of this volcanic activity. Unlike most hydrothermal systems found in the Pacific Ocean, the Magic Mountain site is situated outside the primary rift zone. The source for the hydrothermal fluid that fuels Magic Mountain probably rises along fracture systems associated with a recent episode of rifting that, in turn, followed a massive outpouring of lava. In contrast, the Northern Explorer Ridge has evolved into a complex compound structure consisting of several rift basins bounded by half-graben and arcuate shaped faults with a superimposed pattern of rhombohedral grabens and horst (geology), horsts.
The Explorer Ridge, an mid-ocean ridge, underwater mountain range lying west of Vancouver Island on the Coast of British Columbia, consists of a north-south trending rift zone. It contains one major segment known as the Southern Explorer Ridge, along with other smaller segments, such as the Northern Explorer Ridge. With a depth of , the Southern Explorer Ridge is relatively shallow in comparison with most other rift zones of the northeast Pacific Ocean, indicating there has been considerable volcanic activity along this part of the Explorer Ridge in the past 100,000 years. Magic Mountain (hydrothermal field), Magic Mountain, a large hydrothermal vent area on the Southern Explorer Ridge, is a scene of this volcanic activity. Unlike most hydrothermal systems found in the Pacific Ocean, the Magic Mountain site is situated outside the primary rift zone. The source for the hydrothermal fluid that fuels Magic Mountain probably rises along fracture systems associated with a recent episode of rifting that, in turn, followed a massive outpouring of lava. In contrast, the Northern Explorer Ridge has evolved into a complex compound structure consisting of several rift basins bounded by half-graben and arcuate shaped faults with a superimposed pattern of rhombohedral grabens and horst (geology), horsts.
 The Endeavour Segment, an active rift zone of the larger Juan de Fuca Ridge on the British Columbia Coast, contains a group of active black smokers called the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents, located southwest of Vancouver Island. This group of hydrothermal vents lies below sea level and consists of five hydrothermal fields, known as ''Sasquatch'', ''Saily Dawg'', ''High Rise'', ''Mothra'', and ''Main Endeavour''. Like typical hydrothermal vents, the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents form when cold seawater seeps into cracks and crevices in the Endeavour Segment where it becomes heated by magma that lies beneath the seafloor. As the water is heated, it rises and seeks a path back out into the Pacific Ocean through openings in the Endeavour Segment, forming hydrothermal vents. These hydrothermal vents release fluids with temperatures of over 300 °Celsius, C and have been a focus of research by Canadian and international scientists. The manned United States Navy deep-ocean research submersible DSV Alvin and the remotely operated underwater vehicle Jason (ROV), Jason have done work at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents. Joint Canada-United States studies have made use of the Canadian Remotely Operated Platform for Ocean Sciences. Fisheries and Oceans Canada has conducted extensive acoustic and mooredinstrument programs at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents since 1985.
The Endeavour Segment, an active rift zone of the larger Juan de Fuca Ridge on the British Columbia Coast, contains a group of active black smokers called the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents, located southwest of Vancouver Island. This group of hydrothermal vents lies below sea level and consists of five hydrothermal fields, known as ''Sasquatch'', ''Saily Dawg'', ''High Rise'', ''Mothra'', and ''Main Endeavour''. Like typical hydrothermal vents, the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents form when cold seawater seeps into cracks and crevices in the Endeavour Segment where it becomes heated by magma that lies beneath the seafloor. As the water is heated, it rises and seeks a path back out into the Pacific Ocean through openings in the Endeavour Segment, forming hydrothermal vents. These hydrothermal vents release fluids with temperatures of over 300 °Celsius, C and have been a focus of research by Canadian and international scientists. The manned United States Navy deep-ocean research submersible DSV Alvin and the remotely operated underwater vehicle Jason (ROV), Jason have done work at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents. Joint Canada-United States studies have made use of the Canadian Remotely Operated Platform for Ocean Sciences. Fisheries and Oceans Canada has conducted extensive acoustic and mooredinstrument programs at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents since 1985.
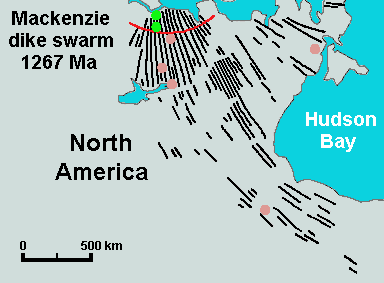 Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River southwest of Coronation Gulf in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive volcanic plateau, lava plateau and
Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River southwest of Coronation Gulf in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive volcanic plateau, lava plateau and  The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province of northern Nunavut forms a large igneous province 95 to 92 million years old in the Canadian Arctic. Part of the larger High Arctic Large Igneous Province, it consists of two volcanic formations called the Ellesmere Island Volcanics and Strand Fiord Formation. In the Strand Fiord Formation, flood basalt lavas reach a thickness of at least . Flood basalts of the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province are similar to terrestrial flood basalts associated with breakup of continents, indicating the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province formed as a result of rifting of the Arctic Ocean and when the large underwater Alpha Ridge was still geologically active.
Widespread basalt volcanism occurred between 60.9 and 61.3 million years ago in the northern Labrador Sea, Davis Strait and in southern Baffin Bay on the eastern coast of Nunavut during the Paleocene period when North America and Greenland were being separated from tectonic movements. This resulted from
The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province of northern Nunavut forms a large igneous province 95 to 92 million years old in the Canadian Arctic. Part of the larger High Arctic Large Igneous Province, it consists of two volcanic formations called the Ellesmere Island Volcanics and Strand Fiord Formation. In the Strand Fiord Formation, flood basalt lavas reach a thickness of at least . Flood basalts of the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province are similar to terrestrial flood basalts associated with breakup of continents, indicating the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province formed as a result of rifting of the Arctic Ocean and when the large underwater Alpha Ridge was still geologically active.
Widespread basalt volcanism occurred between 60.9 and 61.3 million years ago in the northern Labrador Sea, Davis Strait and in southern Baffin Bay on the eastern coast of Nunavut during the Paleocene period when North America and Greenland were being separated from tectonic movements. This resulted from
 The predominantly volcanic Archean and Proterozoic
The predominantly volcanic Archean and Proterozoic 
 The kimberlite
The kimberlite
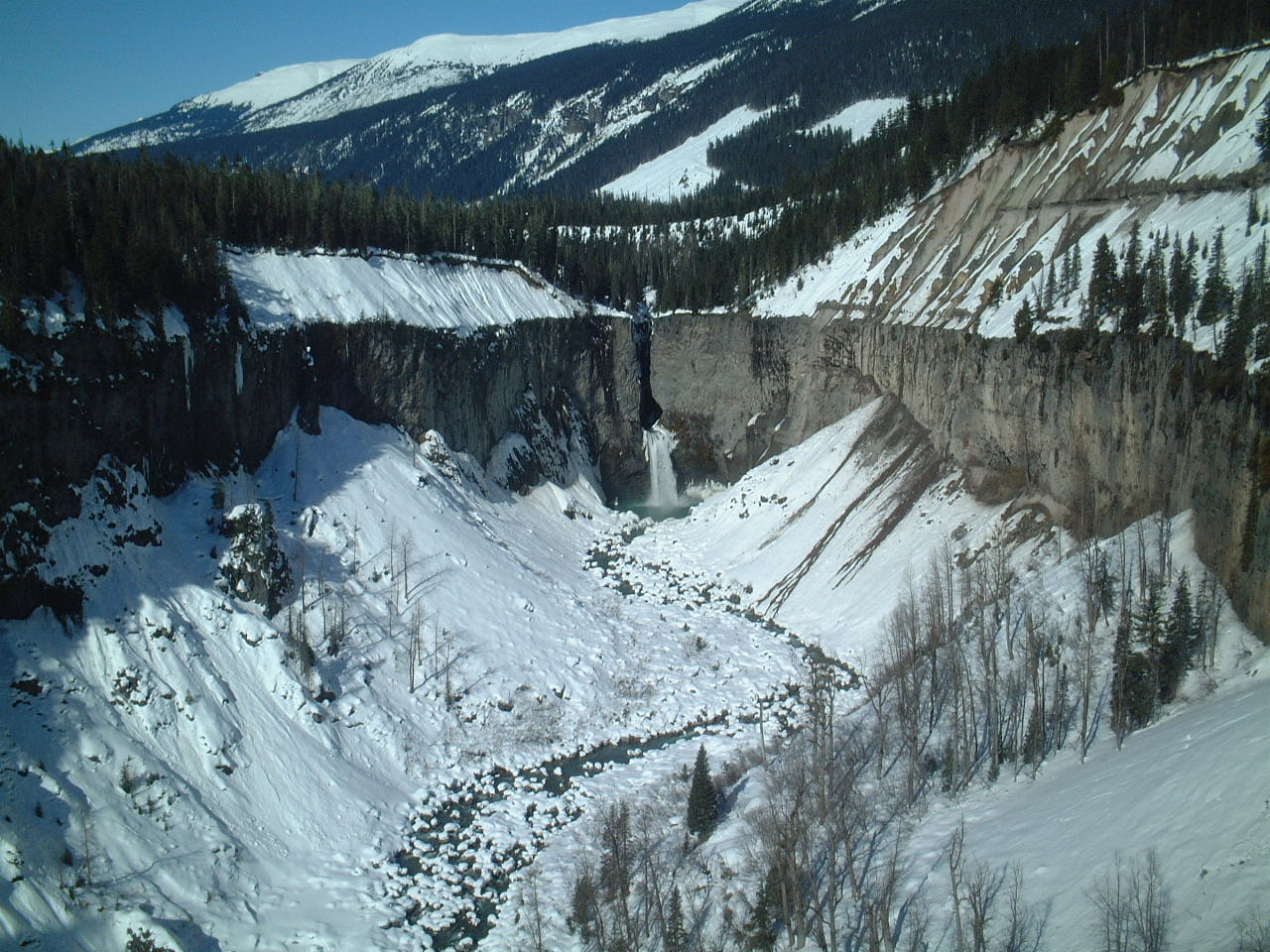

 The Mount Meager massif in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt of southwestern British Columbia was the source for a massive (Volcanic Explosivity Index, VEI-5) Plinian eruption 2,350 years ago similar in character to the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the U.S. state of Washington (U.S. state), Washington. The eruption originated from a vent on the northeast flank of Plinth Peak, the highest and one of four overlapping stratovolcanoes which together form the Mount Meager massif. This activity produced a diverse sequence of volcanic deposits, well exposed in Hill, bluffs along the long Lillooet River, which are grouped as part of the Pebble Creek Formation. The explosive power associated with this Plinian eruption sent an eruption column, ash column estimated to have risen at least above Meager, indicating it entered stratosphere, the second major layer of the Earth's atmosphere. As prevailing winds sent ash and dust as far as to the east, it created the large Bridge River Ash deposit, extending from Mount Meager to central Alberta. Pyroclastic flows travelled downstream from the vent and buried trees along Meager's forested slopes, which were burned in place. An unusual, thick apron of welded Vitrophyre, vitrophyric breccia may represent the explosive collapse of a former
The Mount Meager massif in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt of southwestern British Columbia was the source for a massive (Volcanic Explosivity Index, VEI-5) Plinian eruption 2,350 years ago similar in character to the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the U.S. state of Washington (U.S. state), Washington. The eruption originated from a vent on the northeast flank of Plinth Peak, the highest and one of four overlapping stratovolcanoes which together form the Mount Meager massif. This activity produced a diverse sequence of volcanic deposits, well exposed in Hill, bluffs along the long Lillooet River, which are grouped as part of the Pebble Creek Formation. The explosive power associated with this Plinian eruption sent an eruption column, ash column estimated to have risen at least above Meager, indicating it entered stratosphere, the second major layer of the Earth's atmosphere. As prevailing winds sent ash and dust as far as to the east, it created the large Bridge River Ash deposit, extending from Mount Meager to central Alberta. Pyroclastic flows travelled downstream from the vent and buried trees along Meager's forested slopes, which were burned in place. An unusual, thick apron of welded Vitrophyre, vitrophyric breccia may represent the explosive collapse of a former  The massive Mount Edziza volcanic complex in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northern British Columbia has had more than 20 eruptions throughout the past 10,000 years (Holocene), including Mess Lake Cone, Kana Cone, Cinder Cliff, Icefall Cone, Ridge Cone, Williams Cone, Walkout Creek Cone, Moraine Cone, Sidas Cone, Sleet Cone, Storm Cone, Triplex Cone, Twin Cone, Cache Hill, Camp Hill (British Columbia), Camp Hill, Cocoa Crater, Coffee Crater, Nahta Cone, Tennena Cone, The Saucer, and the well-preserved Eve Cone. Active or recently active hot springs are found in several areas along the western flank of Edziza's lava plateau, including Elwyn springs (36 degree (temperature), °Celsius, C), Taweh springs (46 °C), and inactive springs near Mess Lake. All three hydrothermal areas are near the youngest lava fields on the lava plateau and are probably associated with the most recent volcanic activity at the Mount Edziza volcanic complex. An undated pumice deposit exists throughout the complex estimated to be younger than 500 years.
The massive Mount Edziza volcanic complex in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northern British Columbia has had more than 20 eruptions throughout the past 10,000 years (Holocene), including Mess Lake Cone, Kana Cone, Cinder Cliff, Icefall Cone, Ridge Cone, Williams Cone, Walkout Creek Cone, Moraine Cone, Sidas Cone, Sleet Cone, Storm Cone, Triplex Cone, Twin Cone, Cache Hill, Camp Hill (British Columbia), Camp Hill, Cocoa Crater, Coffee Crater, Nahta Cone, Tennena Cone, The Saucer, and the well-preserved Eve Cone. Active or recently active hot springs are found in several areas along the western flank of Edziza's lava plateau, including Elwyn springs (36 degree (temperature), °Celsius, C), Taweh springs (46 °C), and inactive springs near Mess Lake. All three hydrothermal areas are near the youngest lava fields on the lava plateau and are probably associated with the most recent volcanic activity at the Mount Edziza volcanic complex. An undated pumice deposit exists throughout the complex estimated to be younger than 500 years.
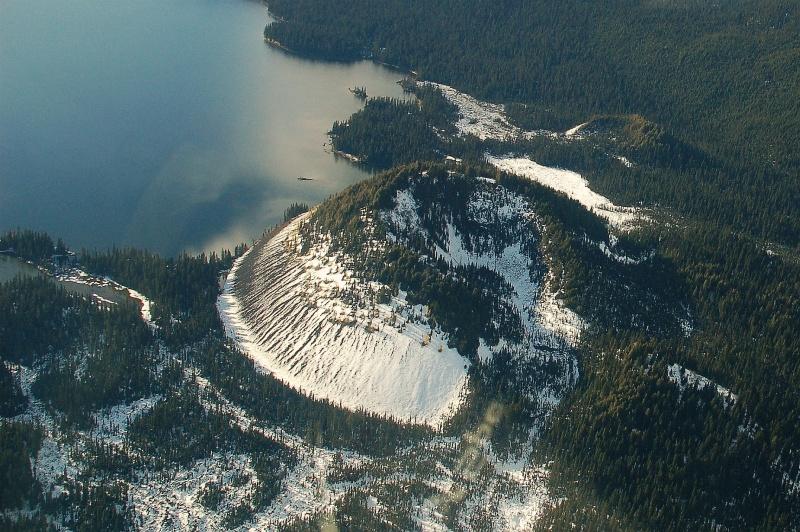 Kostal Cone in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field of east-central British Columbia is a cinder cone responsible for basaltic lava flows comprising a lava bed, damming the southern end of McDougall Lake. There has been activity at this site as recently as 7,600 years ago at Dragon Cone, though more likely less than 1,000 years ago. Kostal Cone is too young for the potassium-argon dating technique (usable on specimens over 100,000 years old), and no charred organic material for radiocarbon dating has been found. However, the uneroded structure of the cone with the existence of trees on its flanks and summit have made it an area for dendrochronology studies, which reveals the growth of tree-ring patterns. Tree-ring dating has revealed an age of about 400 years for Kostal Cone, indicating it formed around 1500. This makes Kostal Cone the youngest volcano in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and thus one of the youngest in Canada.
Kostal Cone in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field of east-central British Columbia is a cinder cone responsible for basaltic lava flows comprising a lava bed, damming the southern end of McDougall Lake. There has been activity at this site as recently as 7,600 years ago at Dragon Cone, though more likely less than 1,000 years ago. Kostal Cone is too young for the potassium-argon dating technique (usable on specimens over 100,000 years old), and no charred organic material for radiocarbon dating has been found. However, the uneroded structure of the cone with the existence of trees on its flanks and summit have made it an area for dendrochronology studies, which reveals the growth of tree-ring patterns. Tree-ring dating has revealed an age of about 400 years for Kostal Cone, indicating it formed around 1500. This makes Kostal Cone the youngest volcano in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and thus one of the youngest in Canada.
 Tseax Cone, a young cinder cone at the southernmost end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, was the source for a major basalt lava flow eruption around the years 1750 and 1775 that travelled into the Tseax River, damming it and forming Lava Lake (British Columbia), Lava Lake. The lava flow subsequently travelled north to the Nass River, where it filled the flat valley floor for an additional , making the entire lava flow long. Native legends from Nisga'a people in the area tell of a prolonged period of disruption by the volcano, including the destruction of two Nisga'a villages known as Lax Ksiluux, British Columbia, Lax Ksiluux and Wii Lax K'abit. Nisga'a people dug pits for shelter but at least 2,000 Nisga'a people were killed due to volcanic gases and poisonous smoke (most likely carbon dioxide). This is Canada's worst known geophysical disaster. It is the only eruption in Canada for which legends of First Nations in Canada, First Nations people have been proven true. As of 1993, the Tseax Cone quietly rests in Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park.
Tseax Cone, a young cinder cone at the southernmost end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, was the source for a major basalt lava flow eruption around the years 1750 and 1775 that travelled into the Tseax River, damming it and forming Lava Lake (British Columbia), Lava Lake. The lava flow subsequently travelled north to the Nass River, where it filled the flat valley floor for an additional , making the entire lava flow long. Native legends from Nisga'a people in the area tell of a prolonged period of disruption by the volcano, including the destruction of two Nisga'a villages known as Lax Ksiluux, British Columbia, Lax Ksiluux and Wii Lax K'abit. Nisga'a people dug pits for shelter but at least 2,000 Nisga'a people were killed due to volcanic gases and poisonous smoke (most likely carbon dioxide). This is Canada's worst known geophysical disaster. It is the only eruption in Canada for which legends of First Nations in Canada, First Nations people have been proven true. As of 1993, the Tseax Cone quietly rests in Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park.
 An eruption was reported by placer mining, placer miners on November 8, 1898 in the Atlin Volcanic Field of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province adjacent to Ruby Mountain volcano south of Gladys Lake when volcanic ash was said to be falling for many days. During the eruption the adjacent placer miners were able to work at nights due to incandescent glow from the eruption. A news report published on December 1, 1898 by the American newspaper publisher The New York Times stated: ''Kinslee and T. P. James, Denver mining men who with Col. Hughes of Rossland have just returned from Alaska, report that a volcano is in active eruption about fifty miles from Atlin City. No name has yet been given to the volcano, but the officials of Atlin are preparing for a trip of inspection and will christen it. It is said to be the second in a string of four mountains lying fifty miles due south of Lake Gladys, all of which are more than 1,400 feet high.'' In 1898 the Atlin, British Columbia, Atlin area was in Alaska boundary dispute, dispute with the Alaska-British Columbia boundary, leading American news broadcasters stating the Atlin area was in Alaska rather than in northwestern British Columbia. This Alaska-British Columbia boundary dispute was eventually resolved by arbitration in 1903 and no evidence for the 1898 eruption has been found, leading researchers to speculate about the eruption and report it as uncertain.
An eruption was reported by placer mining, placer miners on November 8, 1898 in the Atlin Volcanic Field of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province adjacent to Ruby Mountain volcano south of Gladys Lake when volcanic ash was said to be falling for many days. During the eruption the adjacent placer miners were able to work at nights due to incandescent glow from the eruption. A news report published on December 1, 1898 by the American newspaper publisher The New York Times stated: ''Kinslee and T. P. James, Denver mining men who with Col. Hughes of Rossland have just returned from Alaska, report that a volcano is in active eruption about fifty miles from Atlin City. No name has yet been given to the volcano, but the officials of Atlin are preparing for a trip of inspection and will christen it. It is said to be the second in a string of four mountains lying fifty miles due south of Lake Gladys, all of which are more than 1,400 feet high.'' In 1898 the Atlin, British Columbia, Atlin area was in Alaska boundary dispute, dispute with the Alaska-British Columbia boundary, leading American news broadcasters stating the Atlin area was in Alaska rather than in northwestern British Columbia. This Alaska-British Columbia boundary dispute was eventually resolved by arbitration in 1903 and no evidence for the 1898 eruption has been found, leading researchers to speculate about the eruption and report it as uncertain.
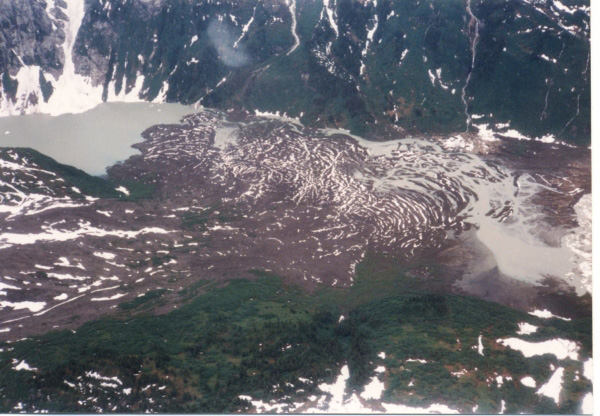 The Volcano (British Columbia), The Volcano at the southern end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province just north of the Alaska-British Columbia boundary is probably the youngest in Canada. It is a poorly built cinder cone made of loose volcanic ash, lapilli-sized tephra and volcanic bombs. Lying above a remote mountain ridge in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it is responsible for lava flow eruptions in 1904 and older that traveled south through river valleys where they crossed the border into the U.S. state of Alaska and dammed the Blue River, a short tributary of the Unuk River. In doing so it formed several small lakes. This eruption had a massive effect on fish, plant and animal inhabitants of the valley, but there is no record of its impact on people, most likely because people were not in the remote area. The entire length of the lava flows are at least and still contain the original lava features from when they were erupted, including pressure ridge (lava), pressure ridges and lava channels. However, sections of the lava flows have collapsed into underlying lava tubes to form cavities. Tephra and scoria from The Volcano covers adjacent mountain ridges and even through it is very young, it has been reduced by erosion from alpine glacial ice found in the heavily glaciated Coast Mountains. The estimated volume of lava and ash from The Volcano is .
The Volcano (British Columbia), The Volcano at the southern end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province just north of the Alaska-British Columbia boundary is probably the youngest in Canada. It is a poorly built cinder cone made of loose volcanic ash, lapilli-sized tephra and volcanic bombs. Lying above a remote mountain ridge in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it is responsible for lava flow eruptions in 1904 and older that traveled south through river valleys where they crossed the border into the U.S. state of Alaska and dammed the Blue River, a short tributary of the Unuk River. In doing so it formed several small lakes. This eruption had a massive effect on fish, plant and animal inhabitants of the valley, but there is no record of its impact on people, most likely because people were not in the remote area. The entire length of the lava flows are at least and still contain the original lava features from when they were erupted, including pressure ridge (lava), pressure ridges and lava channels. However, sections of the lava flows have collapsed into underlying lava tubes to form cavities. Tephra and scoria from The Volcano covers adjacent mountain ridges and even through it is very young, it has been reduced by erosion from alpine glacial ice found in the heavily glaciated Coast Mountains. The estimated volume of lava and ash from The Volcano is .
 A series of 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes, earthquakes of less than magnitude 3.0 were recorded by seismographs in the Baezaeko River region west of Nazko Cone in the Anahim Volcanic Belt on October 9, 2007. The cause of these earthquakes was magma intruding into rock below the surface. Since then more than 1,000 small earthquakes have been recorded. Because of the small size of the earthquake swarms, Natural Resources Canada has added more seismographs in the region for better location and depth accuracy. However, the size and number of the 2007 earthquake swarms indicate there is currently no threat of an eruption. Before magma could erupt in the area adjacent to Nazko Cone, it is expected the size and number of the earthquakes would rise considerably, presaging an eruption.
A series of 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes, earthquakes of less than magnitude 3.0 were recorded by seismographs in the Baezaeko River region west of Nazko Cone in the Anahim Volcanic Belt on October 9, 2007. The cause of these earthquakes was magma intruding into rock below the surface. Since then more than 1,000 small earthquakes have been recorded. Because of the small size of the earthquake swarms, Natural Resources Canada has added more seismographs in the region for better location and depth accuracy. However, the size and number of the 2007 earthquake swarms indicate there is currently no threat of an eruption. Before magma could erupt in the area adjacent to Nazko Cone, it is expected the size and number of the earthquakes would rise considerably, presaging an eruption.
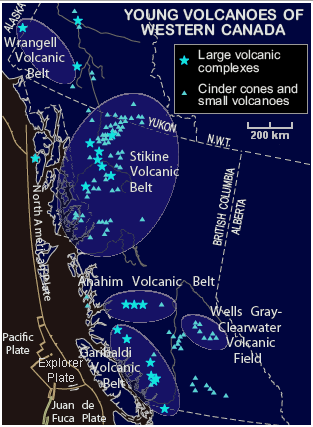 In Canada, even though volcanoes pose significant threats to local communities and any sizable eruption would affect Canada's economy, the work of understanding the frequency and eruption characteristics at volcanoes in Canada is a slow process. This is because most of Canada's dormant and potentially active volcanoes are located in isolated jagged regions, very few scientists study Canadian volcanoes and the provision of money in the Canadian government is limited. Because of these issues, scientists studying Canada's volcanoes have a basic understanding of Canada's volcanic heritage and how it might impact people in the future. Volcanologists are aware that certain areas in Canada have higher levels of volcanic activity than others and how eruptions in these areas might affect people and the environment they live in. When a volcano is showing evidence of volcanic activity, quick action will be required to better understand the process. The lowest possibility for an eruption in Canada per year is approximately 1/200; for a passive lava eruption the possibility is about 1/220, and for a major explosive eruption it is about 1/3333. Even though volcanoes do not seem to be part of the everyday reality of Canadians, recurrent earthquakes and the formation of large
In Canada, even though volcanoes pose significant threats to local communities and any sizable eruption would affect Canada's economy, the work of understanding the frequency and eruption characteristics at volcanoes in Canada is a slow process. This is because most of Canada's dormant and potentially active volcanoes are located in isolated jagged regions, very few scientists study Canadian volcanoes and the provision of money in the Canadian government is limited. Because of these issues, scientists studying Canada's volcanoes have a basic understanding of Canada's volcanic heritage and how it might impact people in the future. Volcanologists are aware that certain areas in Canada have higher levels of volcanic activity than others and how eruptions in these areas might affect people and the environment they live in. When a volcano is showing evidence of volcanic activity, quick action will be required to better understand the process. The lowest possibility for an eruption in Canada per year is approximately 1/200; for a passive lava eruption the possibility is about 1/220, and for a major explosive eruption it is about 1/3333. Even though volcanoes do not seem to be part of the everyday reality of Canadians, recurrent earthquakes and the formation of large  Growing awareness of volcanism, especially the threat from volcanoes in the United States, has led to a number of changes in the way Canadians are dealing with volcanic hazards. For example, The Barrier, an unstable volcanic dam, lava dam retaining the Garibaldi Lake system of southwestern British Columbia, has in the past unleashed several debris flows, most recently in 1855–1856. This led to the evacuation of the small resort village of Garibaldi, British Columbia, Garibaldi nearby and the relocation of residents to new recreational subdivisions away from the hazard zone. Should The Barrier completely collapse, Garibaldi Lake would be entirely released and downstream damage in the Cheakamus River, Cheakamus and Squamish River, Squamish rivers would be considerable, including major damage to the town of Squamish, British Columbia, Squamish and possibly an impact-wave on the waters of Howe Sound that would reach Vancouver Island. The Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan, Canada's volcanic emergency notification program, was established to outline the notification procedure of some of the main agencies that would be involved in response to a volcanic eruption in Canada, an eruption close to Canada's borders, or an eruption significant enough to have an effect on Canada and its people. It focuses primarily on aviation safety because jet aircraft can quickly enter areas of volcanic ash. The program notifies all impacted agencies that have to deal with volcanic events. Aircraft are rerouted away from hazardous ash and people on the ground are notified of potential ash fall.
Growing awareness of volcanism, especially the threat from volcanoes in the United States, has led to a number of changes in the way Canadians are dealing with volcanic hazards. For example, The Barrier, an unstable volcanic dam, lava dam retaining the Garibaldi Lake system of southwestern British Columbia, has in the past unleashed several debris flows, most recently in 1855–1856. This led to the evacuation of the small resort village of Garibaldi, British Columbia, Garibaldi nearby and the relocation of residents to new recreational subdivisions away from the hazard zone. Should The Barrier completely collapse, Garibaldi Lake would be entirely released and downstream damage in the Cheakamus River, Cheakamus and Squamish River, Squamish rivers would be considerable, including major damage to the town of Squamish, British Columbia, Squamish and possibly an impact-wave on the waters of Howe Sound that would reach Vancouver Island. The Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan, Canada's volcanic emergency notification program, was established to outline the notification procedure of some of the main agencies that would be involved in response to a volcanic eruption in Canada, an eruption close to Canada's borders, or an eruption significant enough to have an effect on Canada and its people. It focuses primarily on aviation safety because jet aircraft can quickly enter areas of volcanic ash. The program notifies all impacted agencies that have to deal with volcanic events. Aircraft are rerouted away from hazardous ash and people on the ground are notified of potential ash fall.
Catalogue of Canadian volcanoes
Global Volcanism Program: Volcanoes of Canada and the western USA
GVP: Volcanoes of Canada
Erica A. Massey: A Comparative Study of Glaciovolcanic Palagonitization of Tholeitic and Alkaline Sideromelane in Helgafell, Icland, and Wells Gray-Clearwater Volcanic Filed, BC, Canada. B.Sc., The University of British Columbia, 2014
{{DEFAULTSORT:Volcanism Of Canada Volcanism of Canada, Geographic areas of seismological interest Natural history of Canada Natural hazards in Canada
Volcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
is a major part of the geology of Canada
The geology of Canada is a subject of regional geology and covers the country of Canada, which is the second-largest country in the world. Geologic units and processes are investigated on a large scale to reach a synthesized picture of the geolog ...
and is characterized by many types of volcanic landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
, including lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
flows, volcanic plateau
A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.
Lava plateau
Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions throu ...
s, lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on ...
s, cinder cone
A cinder cone (or scoria cone) is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions o ...
s, stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and per ...
es, shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more v ...
es, submarine volcano
Submarine volcanoes are underwater vents or fissures in the Earth's surface from which magma can erupt. Many submarine volcanoes are located near areas of tectonic plate formation, known as mid-ocean ridges. The volcanoes at mid-ocean ridges ...
es, caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
s, diatreme
A diatreme, sometimes known as a maar-diatreme volcano, is a volcanic pipe formed by a gaseous explosion. When magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the ...
s, and maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow ...
s, along with less common volcanic forms such as tuya
A tuya is a flat-topped, steep-sided volcano formed when lava erupts through a thick glacier or ice sheet. They are rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were covered by glaciers and had active volcanism during the same period.
As lava ...
s and subglacial mound
A subglacial mound (SUGM) is a type of subglacial volcano. This type of volcano forms when lava erupts beneath a thick glacier or ice sheet. The magma forming these volcanoes was not hot enough to melt a vertical pipe right through the overlying ...
s.
Though Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
's volcanic history dates back to the Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
eon, at least 3.11 billion years ago, when its part of the North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
n continent began to form, volcanism continues to occur in Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three Provinces_and_territories_of_Canada#Territories, territor ...
in modern times, where it forms part of an encircling chain of volcanoes and frequent earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s around the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
called the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions and ...
. Because volcanoes in Western and Northern Canada are in relatively remote and sparsely populated areas and their activity is less frequent than with other volcanoes around the Pacific Ocean, Canada is commonly thought to occupy a gap in the Ring of Fire between the volcanoes of the western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
to the south and the Aleutian volcanoes of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
to the north. Even so, the mountainous landscapes of the Canadian provinces of Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
, and the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
include more than 100 volcanoes that have been active during the past two million years and whose eruptions have claimed many lives.
Volcanic activity is responsible for many of Canada's geological and geographical features and mineralization, including the nucleus of the North American continent, known as the Canadian Shield
The Canadian Shield (french: Bouclier canadien ), also called the Laurentian Plateau, is a geologic shield, a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks. It forms the North American Craton (or Laurentia), the anc ...
. Volcanism has led to the formation of hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations across Canada. The country's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents k ...
settings and types of volcanic eruptions
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are oft ...
, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma such ...
s. Canada has a rich record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s, represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarm
A dike swarm (American spelling) or dyke swarm (British spelling) is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes ...
s, sill provinces and layered intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s. The most capable large igneous provinces in Canada are Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
greenstone belt
Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary rocks that occur within Archaean and Proterozoic cratons between granite and gneiss bodies.
The name comes from the green ...
s estimated at 3.8 to 2.5 billion years old, containing a rare volcanic rock called komatiite
Komatiite () is a type of ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rock defined as having crystallised from a lava of at least 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon, potassium and aluminium, and high to extremely high magnesium content. Komatiite wa ...
.
Eruption styles and volcano formations
Eastern Canada
 The 2,677‑million-year-old
The 2,677‑million-year-old Abitibi greenstone belt
The Abitibi greenstone belt is a 2,800-to-2,600-million-year-old greenstone belt that spans across the Ontario–Quebec border in Canada. It is mostly made of volcanic rocks, but also includes ultramafic rocks, mafic intrusions, granitoid rocks, ...
in Ontario and Quebec is one of the largest Archean greenstone belts on Earth and one of the youngest parts of the Superior craton
The Superior Craton is a stable crustal block covering Quebec, Ontario, and southeast Manitoba in Canada, and northern Minnesota in the United States. It is the biggest craton among those formed during the Archean period. A craton is a large part ...
which sequentially forms part of the Canadian Shield.
Komatiite
Komatiite () is a type of ultramafic mantle-derived volcanic rock defined as having crystallised from a lava of at least 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon, potassium and aluminium, and high to extremely high magnesium content. Komatiite wa ...
lavas in the Abitibi greenstone belt (pictured) occur in four lithotectonic assemblages known as Pacaud, Stoughton-Roquemaure, Kidd-Munro and Tisdale. The Swayze greenstone belt The Swayze greenstone belt is a late Archean greenstone belt in northern Ontario, Canada. It is the southwestern extension of the Abitibi greenstone belt.
See also
*Volcanism of Canada
*Volcanism of Eastern Canada
*List of volcanoes in Canada
*List ...
further south is interpreted to be a southwestern extension of the Abitibi greenstone belt.
The Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
Red Lake greenstone belt The Red Lake greenstone belt is an Archean greenstone belt at the town of Red Lake in Northwestern Ontario, Canada. It consists of basaltic and komatiitic volcanics ranging in age from 2,925 to 2,940 million years old and younger rhyolit ...
in western Ontario consists of basaltic and komatiitic volcanics ranging in age from 2,925 to 2,940 million years old and younger rhyolite-andesite volcanics ranging in age from 2,730 to 2,750 million years old. It is situated in the western portion of the Uchi Subprovince The Uchi Subprovince is a Neoarchean volcanic sequence in Manitoba, Canada. It is at the southern margin of the North Caribou terrane and comprises a number of greenstone belts, which contains volcanic rocks that record some 280 million years of vol ...
, a volcanic sequence comprising a number of greenstone belts.
 The 1884- to 1870‑million-year-old
The 1884- to 1870‑million-year-old Circum-Superior Belt
The Circum-Superior Belt is a widespread Paleoproterozoic large igneous province in the Canadian Shield of Northern, Western and Eastern Canada. It extends more than from northeastern Manitoba through northwestern Ontario, southern Nunavut to ...
constitutes a large igneous province extending for more than from the Labrador Trough
The Labrador Trough or the New Quebec Orogen is a long and wide geologic belt in Canada, extending south-southeast from Ungava Bay through Quebec and Labrador.
The trough is a linear belt of sedimentary and volcanic rocks which developed in an ...
in Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
and northeastern Quebec though the Cape Smith Belt The Cape Smith Belt is an early Proterozoic thrust belt in northern Quebec, Canada.
References
Geology of Quebec
{{Canada-geology-stub ...
in northern Quebec, the Belcher Islands
The Belcher Islands ( iu, script=latn, ᓴᓪᓚᔪᒐᐃᑦ, Sanikiluaq) are an archipelago in the southeast part of Hudson Bay near the centre of the Nastapoka arc. The Belcher Islands are spread out over almost . Administratively, they belon ...
in southern Nunavut
Nunavut ( , ; iu, ᓄᓇᕗᑦ , ; ) is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' ...
, the Fox River and Thompson
Thompson may refer to:
People
* Thompson (surname)
* Thompson M. Scoon (1888–1953), New York politician
Places Australia
*Thompson Beach, South Australia, a locality
Bulgaria
* Thompson, Bulgaria, a village in Sofia Province
Canada
* ...
belts in northern Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
, the Winnipegosis komatiite belt
The Winnipegosis komatiite belt is a long and wide greenstone belt located in the Lake Winnipegosis area of central Manitoba, Canada. It has no surface exposure and was identified based on geophysical signatures and drilling during mineral explo ...
in central Manitoba, and on the southern side of the Superior craton in the Animikie Basin of northwestern Ontario. Two volcano-sedimentary sequences exist in the Labrador Trough with ages of 2,170–2,140 million years and 1,883–1,870 million years. In the Cape Smith Belt, two volcanic group
A volcanic group is a stratigraphic group consisting of volcanic strata. They can be in the form of volcanic fields, volcanic complexes and cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequ ...
s range in age from 2,040 to 1,870 million years old called the Povungnituk volcano-sedimentary Group and the Chukotat Group. The Belcher Islands in eastern Hudson Bay contain two volcanic sequences known as the Flaherty and Eskimo volcanics. The Fox River Belt consists of volcanics, sills and sediments some 1,883 million years old while magmatism of the Thompson Belt is dated to 1,880 million years old. To the south lies the 1,864‑million-year-old Winnipegosis komatiites. In the Animikie Basin near Lake Superior, volcanism is dated 1,880 million years old.
 During the
During the Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), ...
era of the Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
eon 1,109 million years ago, northwestern Ontario began to split apart to form the Midcontinent Rift System
The Midcontinent Rift System (MRS) or Keweenawan Rift is a long geological rift in the center of the North American continent and south-central part of the North American plate. It formed when the continent's core, the North American craton, be ...
, also called the Keweenawan Rift. Lava flows created by the rift in the Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
area were formed from basaltic magma. The upwelling of this magma was the result of a hotspot which produced a triple junction
A triple junction is the point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet. At the triple junction each of the three boundaries will be one of three types – a ridge (R), trench (T) or transform fault (F) – and triple junctions can b ...
in the vicinity of Lake Superior. The hotspot made a dome that covered the Lake Superior area. Voluminous basaltic lava flows erupted from the central axis of the rift, similar to the rifting that formed the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. A '' failed arm'' extends north into mainland Ontario where it forms a geological formation known as the Nipigon Embayment. This failed arm includes Lake Nipigon
Lake Nipigon (; french: lac Nipigon; oj, Animbiigoo-zaaga'igan) is part of the Great Lakes drainage basin. It is the largest lake entirely within the boundaries of the Canadian province of Ontario.
Etymology
In the Jesuit Relations the lake is ...
, the largest lake entirely within the boundaries of Ontario.
 Periods of volcanic activity occurred throughout central Canada during the
Periods of volcanic activity occurred throughout central Canada during the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
and Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
periods. The source for this volcanism was a long-lived and stationary area of molten rock called the New England or Great Meteor hotspot. The first event erupted kimberlite magma in the James Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost par ...
lowlands region of northern Ontario 180 million years ago, creating the Attawapiskat kimberlite field The Attawapiskat kimberlite field is a field of kimberlite pipes located astride the Attawapiskat River in the Hudson Bay Lowlands, in Northern Ontario, Canada. It is thought to have formed about 180 million years ago in the Jurassic period when the ...
. Another kimberlite event spanned a period of 13 million years 165 to 152 million years ago, creating the Kirkland Lake kimberlite field The Kirkland Lake kimberlite field is a 165 to 152 million year old kimberlite field in the Kirkland Lake area of northeastern Ontario, Canada.
See also
*Volcanism of Canada
* Volcanism of Eastern Canada
*List of volcanoes in Canada
List of volc ...
in northeastern Ontario. Another period of kimberlite volcanism occurred in northeastern Ontario 154 to 134 million years ago, creating the Lake Timiskaming kimberlite field
The Lake Timiskaming kimberlite field is Canada's southernmost kimberlite field, located in Northeastern Ontario and western Quebec, Canada. It is within the Lake Timiskaming Structural Zone which contains over 50 kimberlite pipes, several of which ...
. As the North American Plate moved westward over the New England hotspot, the New England hotspot created the magma intrusion
In geology, an igneous intrusion (or intrusive body or simply intrusion) is a body of intrusive igneous rock that forms by crystallization of magma slowly cooling below the surface of the Earth. Intrusions have a wide variety of forms and com ...
s of the Monteregian Hills
The Monteregian Hills (french: Collines Montérégiennes) is a linear chain of isolated hills in Montreal and Montérégie, between the Laurentians and the Appalachians.
Etymology
The first definition of the Monteregian Hills came about in 190 ...
in Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
in southern Quebec. These intrusive stocks have been variously interpreted as the feeder intrusions of long extinct volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
es that would have been active 125 million years ago, or as intrusions that never breached the surface in volcanic activity. The lack of a noticeable hotspot track west of the Monteregian Hills might be due either to failure of the New England mantle plume to pass through massive strong rock of the Canadian Shield, the lack of noticeable intrusions, or to strengthening of the New England mantle plume when it approached the Monteregian Hills region.
About 250 million years ago during the early Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
period, Atlantic Canada lay roughly in the middle of a giant continent called Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. This supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
began to fracture 220 million years ago when the Earth's lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
was being pulled apart from extensional stress, creating a divergent plate boundary
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent b ...
known as the Fundy Basin
The Fundy Basin is a sediment-filled rift basin on the Atlantic coast of southeastern Canada. It contains three sub-basins; the Fundy sub-basin, the Minas Basin and the Chignecto Basin. These arms meet at the Bay of Fundy, which is contained with ...
. The focus of the rifting began somewhere between where present-day eastern North America and northwestern Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
were joined. During the formation of the Fundy Basin, volcanic activity never stopped as shown by the going eruption of lava along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North Ame ...
; an underwater volcanic mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
formed as a result of continuous seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
History of study
Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener an ...
between eastern North America and northwestern Africa. As the Fundy Basin continued to form 201 million years ago, a series of basaltic lava flows were erupted, forming a volcanic mountain range on the mainland portion of southwestern Nova Scotia known as North Mountain, stretching from Brier Island
Brier Island is an island in the Bay of Fundy in Digby County, Nova Scotia.
Geography
The island is the westernmost part of Nova Scotia and the southern end of the North Mountain ridge with Long Island lying immediately northeast; both islands ...
in the south to Cape Split
Cape Split is a headland located on the Bay of Fundy coast of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. The Battle off Cape Split happened during the American Revolution.
Cape Split is located in Kings County and is a continuation of the North Mo ...
in the north. This series of lava flows cover most of the Fundy Basin and extend under the Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is the hi ...
where parts of it are exposed on the shore at the rural community of Five Islands, east of Parrsboro
Parrsboro is a community located in Cumberland County, Nova Scotia, Canada.
A regional service centre for southern Cumberland County, the community is also known for its port on the Minas Basin, the Ship's Company Theatre productions, and the ...
on the north side of the bay. Large dikes wide exist throughout southernmost New Brunswick with ages and compositions similar to the North Mountain basalt, indicating these dikes were the source for North Mountain lava flows. However, North Mountain is the remnants of a larger volcanic feature that has now been largely eroded based on the existence of basin border faults and erosion. The hard basaltic ridge of North Mountain resisted the grinding of ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Las ...
s that flowed over this region during the past ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
s, and now forms one side of the Annapolis Valley
The Annapolis Valley is a valley and region in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is located in the western part of the Nova Scotia peninsula, formed by a trough between two parallel mountain ranges along the shore of the Bay of Fundy. St ...
in the western part of the Nova Scotia peninsula
The Nova Scotia peninsula is a peninsula on the Atlantic coast of North America.
Location
The Nova Scotia peninsula is part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada and is connected to the neighbouring province of New Brunswick through the Isth ...
. The layering of a North Mountain lava flow less than thick at McKay Head, closely resemble that of some Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
an lava lake
Lava lakes are large volumes of molten lava, usually basaltic, contained in a volcanic vent, crater, or broad depression. The term is used to describe both lava lakes that are wholly or partly molten and those that are solidified (sometim ...
s, indicating Hawaiian eruption
A Hawaiian eruption is a type of volcanic eruption where lava flows from the vent in a relatively gentle, low level eruption; it is so named because it is characteristic of Hawaiian volcanoes. Typically they are effusive eruptions, with basaltic ...
s occurred during the formation of North Mountain.
 The
The Fogo Seamounts
The Fogo Seamounts, also called the Fogo Seamount Chain, are a group of undersea mountains southeast of the Grand Banks of Newfoundland in the North Atlantic Ocean. This seamount chain, lying approximately offshore from the island of Newfoundlan ...
, located offshore of Newfoundland to the southwest of the Grand Banks
The Grand Banks of Newfoundland are a series of underwater plateaus south-east of the island of Newfoundland on the North American continental shelf. The Grand Banks are one of the world's richest fishing grounds, supporting Atlantic cod, swordf ...
, consists of submarine volcanoes with dates extending back to the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
period at least 143 million years ago. They may have one or two origins. The Fogo Seamounts could have formed along fracture zones in the Atlantic seafloor because of the large number of seamounts on the North American continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
. The other explanation for their origin is they formed above a mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
associated with the Canary
Canary originally referred to the island of Gran Canaria on the west coast of Africa, and the group of surrounding islands (the Canary Islands). It may also refer to:
Animals Birds
* Canaries, birds in the genera ''Serinus'' and ''Crithagra'' i ...
or Azores hotspot
The Azores hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. The Azores is relatively young and is associated with a bathymetric swell, a gravity anomaly and ocean island basalt geochemistry. The Azores hotspot lies just east of the ...
s in the Atlantic Ocean, based on the existence of older seamounts to the northwest and younger seamounts to the southeast. The existence of flat-topped seamounts throughout the Fogo Seamount chain indicate some of these seamounts would once have stood above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
as islands that would have been volcanically active. Their flatness is due to coastal erosion, such as waves and winds. Other submarine volcanoes offshore of Eastern Canada include the poorly studied Newfoundland Seamounts
The Newfoundland Seamounts are a group of seamounts offshore of Eastern Canada in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Named for the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, this group of seamounts formed during the Cretaceous period and are poorly ...
.
Western Canada
TheFlin Flon greenstone belt
The Flin Flon greenstone belt, also referred to as the Flin Flon – Snow Lake greenstone belt, is a Precambrian greenstone belt located in the central area of Manitoba and east-central Saskatchewan, Canada (near Flin Flon). It lies in the central ...
in central Manitoba and east-central Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
is a collage of deformed volcanic arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate,
with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc lo ...
rocks ranging in age from 1,904 to 1,864 million years old during the Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions (eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ...
sub-division of the Precambrian eon. Volcanic activity between 1,890 and 1,864 million years ago produced calc-alkaline
The calc-alkaline magma series is one of two main subdivisions of the subalkaline magma series, the other subalkaline magma series being the tholeiitic series. A magma series is a series of compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic mag ...
andesite-rhyolite magmas and rare shoshonite
Shoshonite is a type of igneous rock. More specifically, it is a potassium-rich variety of basaltic trachyandesite, composed of olivine, augite and plagioclase phenocrysts in a groundmass with calcic plagioclase and sanidine and some dark-colored v ...
and trachyandesite magmas while the 1,904‑million-year-old arc volcanism occurred in one or more separate volcanic arcs that were possibly characterized by rapid subduction of thin oceanic crust and large back-arc basin
A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of ...
s. In contrast, the younger 1,890‑million-year-old volcanics indicate evidence of crustal thickening. This was due to long-term growth of the volcanic arcs by continuous volcanic activity and tectonic thickening associated with arc collisions and successive arc deformation. This in turn followed a massive mountain building event called the Trans-Hudson orogeny
The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the North American Craton (also called Laurentia), forging the initial North American continen ...
.
The Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
period 145-66 million years ago was a period for active kimberlite volcanism in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin
The Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) underlies of Western Canada including southwestern Manitoba, southern Saskatchewan, Alberta, northeastern British Columbia and the southwest corner of the Northwest Territories. This vast sedimentary ...
of Alberta and Saskatchewan. The Fort à la Corne kimberlite field in central Saskatchewan formed 104 to 95 million years ago during the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
. Unlike most kimberlite fields on Earth, the Fort à la Corne kimberlite field formed during more than one eruptive event. Its kimberlites are among the most complete examples on Earth, preserving kimberlite pipes and maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow ...
volcanoes. The Northern Alberta kimberlite province
The northern Alberta kimberlite province (NAKP) consists of three groups of diatremes or volcanic pipes in northern Alberta, north-central Alberta, Canada, most of which are kimberlites and some of which are diamondiferous. They are called the ...
consists of three kimberlite fields known as the Birch Mountains
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech-oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 3 ...
, Buffalo Head Hills and the Mountain Lake cluster
The Mountain Lake cluster consists of two diatremes or volcanic pipes in Northern Alberta, Canada. It was emplaced during a period of kimberlite volcanism in the Late Cretaceous epoch.
Although they were originally described as kimberlite or kimb ...
. The Birch Mountains kimberlite field consists of eight kimberlite pipes known as Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
, Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
, Xena
Xena is a fictional character from Robert Tapert's '' Xena: Warrior Princess'' franchise. Co-created by Tapert and John Schulian, she first appeared in the 1995–1999 television series ''Hercules: The Legendary Journeys'', before going on to ...
, Legend
A legend is a Folklore genre, genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived, both by teller and listeners, to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human valu ...
and Valkyrie
In Norse mythology, a valkyrie ("chooser of the slain") is one of a host of female figures who guide souls of the dead to the god Odin's hall Valhalla. There, the deceased warriors become (Old Norse "single (or once) fighters"Orchard (1997:36) ...
, dating approximately 75 million years old. The Buffalo Head Hills kimberlite field was dominated by explosive kimberlite volcanism from 88 million years ago to 81 million years ago, forming maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow ...
s. Kimberlites of the Buffalo Head Hills field are similar to those associated with the Fort à la Corne kimberlite field in central Saskatchewan. The kimberlite pipes of the Mountain Lake cluster were formed during a similar timespan with the Birch Mountains field 77 million years ago.
Formation of the Pacific Northwest
 The Canadian portion of the
The Canadian portion of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
began forming during the early Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
period when a group of active volcanic islands collided against a pre-existing continental margin
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin ...
and coastline of Western Canada. These volcanic islands, known as the Intermontane Islands
The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active volcanic islands somewhere in the Pacific Ocean during the Triassic time beginning around 245 million years ago. They were 600 to long and rode atop a microplate known as the Intermontane Plate ...
by geoscientists, were formed on a pre-existing tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
called the Intermontane Plate
The Intermontane Plate was an ancient oceanic tectonic plate that lay on the west coast of North America about 195 million years ago. The Intermontane Plate was surrounded by a chain of volcanic islands called the Intermontane Islands, which had b ...
about 245 million years ago by subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
of the former Insular Plate to its west during the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
period. This subduction zone records another subduction zone called the Intermontane Trench
The Intermontane Trench was an ancient oceanic trench during the Triassic. The trench was probably long, parallel to the west coast of North America. The ocean that the trench was located in was called the Slide Mountain Ocean.
See also
*Inter ...
under an ancient ocean between the Intermontane Islands and the former continental margin of Western Canada called the Slide Mountain Ocean
The Slide Mountain Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America beginning around 245 million years ago in the Triassic period. It is named after the Slide Mountain Terrane, which is composed of rocks f ...
. This arrangement of two parallel subduction zones is unusual in that very few twin subduction zones exist on Earth; the Philippine Mobile Belt
In the geology of the Philippines, the Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction z ...
off the eastern coast of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
is an example of a modern twin subduction zone. As the Intermontane Plate drew closer to the pre-existing continental margin by ongoing subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
under the Slide Mountain Ocean, the Intermontane Islands drew closer to the former continental margin and coastline of Western Canada, supporting a volcanic arc on the former continental margin of Western Canada. As the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific ...
drifted west and the Intermontane Plate continued to drift east to the ancient continental margin of Western Canada, the Slide Mountain Ocean began to close by ongoing subduction under the Slide Mountain Ocean. This subduction zone eventually jammed and shut down completely about 180 million years ago, ending the arc volcanism on the ancient continental margin of Western Canada and the Intermontane Islands collided, forming a long chain of deformed volcanic and sedimentary rock called the Intermontane Belt
The Intermontane Belt is a physiogeological region in the Pacific Northwest of North America, stretching from northern Washington into British Columbia, Yukon, and Alaska. It comprises rolling hills, high plateaus and deeply cut valleys. The roc ...
, which consists of deeply cut valleys, high plateaus, and rolling uplands. This collision also crushed and folded sedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock (geology), rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic matter, organic particles at Earth#Surface, Earth's surface, followed by cementation (geology), cementation. Sedimentati ...
and igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main The three types of rocks, rock types, the others being Sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rock ...
s, creating a mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
called the Kootenay Fold Belt which existed in far eastern British Columbia.
 After the sedimentary and igneous rocks were folded and crushed, it resulted in the creation of a new continental shelf and coastline. The Insular Plate continued to subduct under the new continental shelf and coastline about 130 million years ago during the mid
After the sedimentary and igneous rocks were folded and crushed, it resulted in the creation of a new continental shelf and coastline. The Insular Plate continued to subduct under the new continental shelf and coastline about 130 million years ago during the mid Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
period after the formation of the Intermontane Belt, supporting a new continental volcanic arc called the Omineca Arc. Magma rising from the Omineca Arc successfully connected the Intermontane Belt to the mainland of Western Canada, forming a chain of volcanoes in British Columbia that existed discontinuously for about 60 million years. The ocean lying offshore during this period is called the Bridge River Ocean. It was also during this period when another group of active volcanic islands existed along the newly built continental shelf and coastline. These volcanic islands, known as the Insular Islands
The Insular Islands were an extended chain of volcanic islands forming an arc in what is now the Pacific Ocean during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras. The islands formed by subduction and melting of the Farallon Plate along a fragment (or micropla ...
, were formed on the Insular Plate by subduction of the former Farallon Plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate. It formed one of the three main plates of Panthalassa, alongside the Phoenix Plate and Izanagi Plate, which were connected by a triple junction. The Farallon Plate began subducting under the west c ...
to its west during the early Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
era. As the North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific ...
drifted west and the Insular Plate drifted east to the continental margin of Western Canada, the Bridge River Ocean began to close by ongoing subduction under the Bridge River Ocean. This subduction zone eventually jammed and shut down completely 115 million years ago, ending the Omineca Arc volcanism and the Insular Islands collided, forming the Insular Belt
The Insular Belt is a physical geography, physiogeological region on the north western North American coast. It consists of three major island groups and many smaller islands and stretches from southern British Columbia into Alaska and the Yukon. I ...
. Compression resulting from this collision crushed, fractured and folded rocks along the continental margin. The Insular Belt then welded onto the continental margin by magma that eventually cooled to create a large mass of igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main The three types of rocks, rock types, the others being Sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rock ...
, creating a new continental margin. This large mass of igneous rock is the largest granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
outcropping in North America.
 The Farallon Plate continued to subduct under the new continental margin of Western Canada after the Insular Plate and Insular Islands collided with the former continental margin, supporting a new chain of volcanoes on the mainland of Western Canada called the
The Farallon Plate continued to subduct under the new continental margin of Western Canada after the Insular Plate and Insular Islands collided with the former continental margin, supporting a new chain of volcanoes on the mainland of Western Canada called the Coast Range Arc
The Coast Range Arc was a large volcanic arc system, extending from northern Washington through British Columbia and the Alaska Panhandle to southwestern Yukon. The Coast Range Arc lies along the western margin of the North American Plate in the P ...
about 100 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
epoch. Magma ascending from the Farallon Plate under the new continental margin burned their way upward through the newly accreted Insular Belt, injecting huge quantities of granite into older igneous rocks of the Insular Belt. At the surface, new volcanoes were built along the continental margin. The basement of this arc was likely Early Cretaceous and Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987.
In European lithostratigraphy, the name ...
age intrusions from the Insular Islands.
 One of the major aspects that changed early during the Coast Range Arc was the status of the northern end of the Farallon Plate, a portion now known as the
One of the major aspects that changed early during the Coast Range Arc was the status of the northern end of the Farallon Plate, a portion now known as the Kula Plate
The Kula Plate was an oceanic tectonic plate under the northern Pacific Ocean south of the Near Islands segment of the Aleutian Islands. It has been subducted under the North American Plate at the Aleutian Trench, being replaced by the Pacific Pla ...
. About 85 million years ago, the Kula Plate broke off from the Farallon Plate to form an area of seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
History of study
Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener an ...
called the Kula-Farallon Ridge
The Kula-Farallon Ridge was an ancient mid-ocean ridge that existed between the Kula and Farallon plates in the Pacific Ocean during the Jurassic period. There was a small piece of this ridge off the Pacific Northwest 43 million years ago. The r ...
. This change apparently had some important ramifications for regional geologic evolution. When this change was completed, Coast Range Arc volcanism returned and sections of the arc were uplifted considerably in latest Cretaceous time. This started a period of mountain building that affected much of western North America called the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
. In particular a large area of dextral transpression and southwest-directed thrust faulting was active from 75 to 66 million years ago. Much of the record of this deformation has been overridden by Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
age structures and the zone of Cretaceous dextral thrust faulting appears to have been widespread. It was also during this period when massive amounts of molten granite intruded highly deformed ocean rocks and assorted fragments from pre-existing island arcs, largely remnants of the Bridge River Ocean. This molten granite burned the old oceanic sediments into a glittering medium-grade metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
called schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes o ...
. The older intrusions of the Coast Range Arc were then deformed under the heat and pressure of later intrusions, turning them into layered metamorphic rock known as gneiss
Gneiss ( ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. Gneiss forms at higher temperatures an ...
. In some places, mixtures of older intrusive rocks and the original oceanic rocks have been distorted and warped under intense heat, weight and stress to create unusual swirled patterns known as migmatite
Migmatite is a composite rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments, commonly within Precambrian cratonic blocks. It consists of two or more constituents often layered repetitively: one layer is an older metamorphic rock tha ...
, appearing to have been nearly melted in the procedure.
Volcanism began to decline along the length of the arc about 60 million years ago during the Albian
The Albian is both an age of the geologic timescale and a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the youngest or uppermost subdivision of the Early/Lower Cretaceous Epoch/Series. Its approximate time range is 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma to 100.5 ± 0.9 M ...
and Aptian
The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma (million years ago), a ...
faunal stage
In chronostratigraphy, a stage is a succession of rock strata laid down in a single age on the geologic timescale, which usually represents millions of years of deposition. A given stage of rock and the corresponding age of time will by conventi ...
s of the Cretaceous period. This resulted from the changing geometry of the Kula Plate, which progressively developed a more northerly movement along the mainland of Western Canada. Instead of subducting beneath Western Canada, the Kula Plate began subducting underneath southwestern Yukon and Alaska during the early Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
period. Volcanism along the entire length of the Coast Range Arc shut down about 50 million years ago and many of the volcanoes have disappeared from erosion. What remains of the Coast Range Arc to this day are outcrops of granite when magma intruded and cooled at depth beneath the volcanoes, forming the Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains (french: La chaîne Côtière) are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia ...
. During construction of intrusions 70 and 57 million years ago, the northern motion of the Kula Plate might have been between and per year. However, other geologic studies determined the Kula Plate moved at a rate as fast as per year.
Cascadia subduction zone complexes
 As the last of the Kula Plate decayed and the Farallon Plate advanced back into this area from the south, it once again started to subduct under the continental margin of Western Canada 37 million years ago, supporting a chain of volcanoes called the
As the last of the Kula Plate decayed and the Farallon Plate advanced back into this area from the south, it once again started to subduct under the continental margin of Western Canada 37 million years ago, supporting a chain of volcanoes called the Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanoes (also known as the Cascade Volcanic Arc or the Cascade Arc) are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern Califo ...
. At least four volcanic formations along the British Columbia Coast
, settlement_type = Region of British Columbia
, image_skyline =
, nickname = "The Coast"
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 = British ...
are associated with Cascadia subduction zone volcanism. The oldest is the eroded 18-million-year-old Pemberton Volcanic Belt which extends west-northwest from south-central British Columbia to Haida Gwaii in the northeast where it lies west of mainland British Columbia. In the south it is defined by a group of epizonal intrusions and a few erosional remnants of eruptive rock. Farther north in the large Ha-Iltzuk Icefield, Ha-Iltzuk and Waddington icefields, it includes two large dissected calderas called Silverthrone Caldera and Franklin Glacier Complex while Haida Gwaii to the northeast contains a volcanic formation (stratigraphy), formation ranging in age from Miocene to Pliocene called the Masset Formation. Although widely separated from each other, all Pemberton Belt rocks are of similar age and have similar magma compositions. Therefore, these magmatic rocks are believed to be products of arc volcanism related to subduction of the Farallon Plate. By late Pliocene time the Farallon Plate had been greatly reduced in size and its northern portion ultimately broke off between five and seven million years ago to form a new plate boundary called the Nootka Fault. This rupture created the two small Juan de Fuca Plate, Juan de Fuca and Explorer Plate, Explorer plates that lie off the west coast of Vancouver Island.
 The four-million-year-old Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, a north-south trending zone of volcanoes and volcanic rock in the southern
The four-million-year-old Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, a north-south trending zone of volcanoes and volcanic rock in the southern Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains (french: La chaîne Côtière) are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia ...
of southwestern British Columbia, can be grouped into at least three enechelon segments, referred to as the northern, central, and southern segments. The northern segment overlaps the older Pemberton Volcanic Belt at a low angle near the Mount Meager massif where Garibaldi Belt lavas rest on uplifted and deeply eroded remnants of Pemberton Belt subvolcanic rock, subvolcanic intrusions and combines to form a single belt. A few isolated volcanoes northwest of the Mount Meager massif, such as Silverthrone Caldera and Franklin Glacier Complex, are also grouped as part of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt. However, their tectonic origins are largely unexplained and are a matter of going research. When the Farallon Plate ruptured to create the Nootka Fault between five and seven million years ago, there were some apparent changes along the Cascadia subduction zone. At issue is the current plate configuration and rate of subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
but based on rock composition is for Silverthrone Caldera and Franklin Glacier Complex to be subduction related. The roughly circular, wide, deeply dissected Silverthrone Caldera in the northern segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, was formed one million years ago during the Early Pleistocene period. The bulk of the volcano was erupted 0.4 million years ago, but younger phases, consisting of lava flows and subsidiary volcanoes with compositions of andesite and basaltic andesite are also present. Mount Silverthrone, an eroded lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on ...
on the northeast edge of Silverthrone Caldera, was episodically active during both Pemberton and Garibaldi stages of volcanism. The eroded Franklin Glacier Complex just to the southeast consists of dacite and andesite rocks that range in age from 3.9 to 2.2 million years old. Southeast of Franklin Glacier Complex, the Bridge River Cones comprise remnants of both andesitic and alkali basalt cones and lava flows. These range in age from about one million years old to 0.5 million years old and commonly display ice-contact features related to subglacial eruptions. The Mount Meager massif, the most persistent volcano in the northern portion of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, is a complex of at least four overlapping stratovolcanoes made of dacite and rhyodacite that become progressively younger from south to north, ranging in age from two million to 2,490 years old. The central segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt is defined by a group of eight volcanoes on a ridge of highland east of the Squamish River, and by remnants of basaltic lava flows preserved in the adjacent Squamish valley. Mount Cayley, the largest and most persistent volcano, is a deeply eroded stratovolcano comprising a lava dome complex made of dacite and minor rhyodacite ranging in age from 3.8 to 0.31 million years old. Mount Fee, a narrow volcanic plug made of rhyodacite about long and wide, rises above the highland ridge. Complete denudation of the central spine as well as the absence of till under lava flows from Mount Fee suggest a preglacial age. The other volcanoes of the central Garibaldi Belt, including Ember Ridge, Pali Dome, Cauldron Dome, Slag Hill, Mount Brew (Cheakamus River), Mount Brew and Ring Mountain (British Columbia), Crucible Dome, were formed during subglacial eruptions to develop tuya-like forms with over-steepened, ice-contact margins. The primary volcanoes in the southern segment are Mount Garibaldi, Mount Price (British Columbia), Mount Price, and The Black Tusk. The oldest volcano, The Black Tusk, is the remnants of an extinct andesitic stratovolcano that formed during two distant stages of volcanic activity, the first between 1.1 and 1.3 million years ago and the second between 0.17 and 0.21 million years ago. Mount Garibaldi, a fairly dissected stratovolcano north of Vancouver, was built by Peléan eruptions between 0.26 and 0.22 million years ago during the waning stages of the last glacial period, last glacial, or "Wisconsinian", period. Mount Price, a less significant stratovolcano just north of Mount Garibaldi, formed during three distinct periods of volcanic activity beginning at 1.2 million years ago and culminating with the eruption of Clinker Peak on its western flank 0.3 million years ago. In addition to the large, central andesite-dacite volcanoes, the southern portion of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt includes remnants of basalt and basaltic andesite lava flows and pyroclastic rocks. These include valley -filling lava flows interbedded with till containing wood about 34,000 years old.
The poorly studied Alert Bay Volcanic Belt extends from Brooks Peninsula on the northwestern coast of Vancouver Island to Port McNeill, British Columbia, Port McNeill on the northeastern coast of Vancouver Island. It encompasses several separate remnants of late Neogene volcanic piles and related intrusions ranging in composition from basalt to rhyolite and in age from about eight million years old in the west to about 3.5 million years old elsewhere. Major element analyses of Alert Bay volcanic and hypabyssal rocks suggest two different basalt-andesite-dacite-rhyolite suites with divergent fractionation trends. The first coincides with the typical calc-alkaline, Cascade trend, whereas the other is more alkaline and more Fe-enriched following a trend which straddles the calc-alkaline-tholeiite boundary. The western end of the Alert Bay Volcanic Belt is now about northeast of the Nootka Fault. However, at the time of its formation the volcanic belt may have been coincident with the subducted plate boundary. Also, the timing of volcanism corresponds to shifts of plate motion and changes in the locus of volcanism along the Pemberton and Garibaldi volcanic belts. This brief interval of plate motion adjustment at about 3.5 million years ago may have triggered the generation of basaltic magma along the descending plate edge. Because the Alert Bay Volcanic Belt has not been active for at least 3.5 million years, volcanism in the Alert Bay Volcanic Belt is probably extinct.
 The Chilcotin Group, a large igneous province and volcanic plateau in south-central British Columbia, consists of thin, flat-lying, poorly formed columnar basalt lava flows that have formed as a result of partial melting in a weak zone in the upper part of the Earth's mantle (geology), mantle within a
The Chilcotin Group, a large igneous province and volcanic plateau in south-central British Columbia, consists of thin, flat-lying, poorly formed columnar basalt lava flows that have formed as a result of partial melting in a weak zone in the upper part of the Earth's mantle (geology), mantle within a back-arc basin
A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of ...
related to subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate. Chilcotin Group volcanism occurred in three distant magmatic episodes, the first 16-14 million years ago, the seconed 10-6 million years ago and the third 3-1 million years ago. Anahim Peak, a volcanic plug near the eastern flank of the Rainbow Range, and other plugs penetrating the Chilcotin Group are suggested to be vents for basalt volcanism. These volcanic plugs form a northwest trend about inland from the Pemberton and Garibaldi volcanic belts and exist along the axis of the volcanic plateau. Silicic tuff lying between Chilcotin basalt lava flows, likely originated from explosive eruption
In volcanology, an explosive eruption is a volcanic eruption of the most violent type. A notable example is the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Such eruptions result when sufficient gas has dissolved under pressure within a viscous magma such ...
s related to arc volcanism in the Garibaldi and Pemberton belts just to the west and was preserved between successive basaltic lava eruptions in the Chilcotin back-arc basin. It is suggested by geoscientists the Chilcotin Group forms a sequence of merged low-profile shield volcanoes erupted from central vents.
British Columbia plume and rift complexes
 The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northwestern British Columbia, also called the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is the most active volcanic region in Canada. It comprises a large number of small cinder cones and associated lava plains, and three large, compositionally diverse volcanoes, known as the Level Mountain, the Mount Edziza volcanic complex, and Hoodoo Mountain. In the south the volcanic province is somewhat narrow and crosses diagonally through the northwesterly structural trend of the Coast Mountains. Farther north it is less clearly defined, forming a large arch that swings westward through central Yukon. Volcanoes within the British Columbia portion of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are disposed along short, northerly trending en-echelon segments which, in the British Columbia portion of the volcanic province, are unmistakably involved with north-trending rift structures including synvolcanic grabens and half-grabens similar to the East African Rift, which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward across eastern Africa. The Northern Cordilleran rift system formed as a result of the North American continent being stretched by extensional forces as the Pacific Plate slides northward along the Queen Charlotte Fault to the west, on its way to the Aleutian Trench, which extends along the southern coastline of Alaska and the adjacent waters of northeastern Siberia off the coast of Kamchatka Peninsula. As the continental crust stretches, the near-surface rocks fracture along steeply dipping cracks parallel to the rift known as fault (geology), faults. Hot basaltic magma rises along these fractures to create passive lava eruptions. The compositions of lavas in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are mantle-derived alkali olivine basalt, lesser hawaiite and basanite, which form the large shield volcanoes and small cinder cones throughout the volcanic province. Many of them contain inclusions of lherzolite. The large central volcanoes of the volcanic province consist largely of trachyte, pantellerite, and comendite lavas. These lava compositions were formed by fractionation of primary alkali basalt magma in crustal reservoirs. A region of continental rifting, such as the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, would support the development of high-level reservoirs of sufficient size and thermal capacity to sustain prolonged fractionation.
The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northwestern British Columbia, also called the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is the most active volcanic region in Canada. It comprises a large number of small cinder cones and associated lava plains, and three large, compositionally diverse volcanoes, known as the Level Mountain, the Mount Edziza volcanic complex, and Hoodoo Mountain. In the south the volcanic province is somewhat narrow and crosses diagonally through the northwesterly structural trend of the Coast Mountains. Farther north it is less clearly defined, forming a large arch that swings westward through central Yukon. Volcanoes within the British Columbia portion of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are disposed along short, northerly trending en-echelon segments which, in the British Columbia portion of the volcanic province, are unmistakably involved with north-trending rift structures including synvolcanic grabens and half-grabens similar to the East African Rift, which extends from the Afar Triple Junction southward across eastern Africa. The Northern Cordilleran rift system formed as a result of the North American continent being stretched by extensional forces as the Pacific Plate slides northward along the Queen Charlotte Fault to the west, on its way to the Aleutian Trench, which extends along the southern coastline of Alaska and the adjacent waters of northeastern Siberia off the coast of Kamchatka Peninsula. As the continental crust stretches, the near-surface rocks fracture along steeply dipping cracks parallel to the rift known as fault (geology), faults. Hot basaltic magma rises along these fractures to create passive lava eruptions. The compositions of lavas in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province are mantle-derived alkali olivine basalt, lesser hawaiite and basanite, which form the large shield volcanoes and small cinder cones throughout the volcanic province. Many of them contain inclusions of lherzolite. The large central volcanoes of the volcanic province consist largely of trachyte, pantellerite, and comendite lavas. These lava compositions were formed by fractionation of primary alkali basalt magma in crustal reservoirs. A region of continental rifting, such as the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, would support the development of high-level reservoirs of sufficient size and thermal capacity to sustain prolonged fractionation.
 The Explorer Ridge, an mid-ocean ridge, underwater mountain range lying west of Vancouver Island on the Coast of British Columbia, consists of a north-south trending rift zone. It contains one major segment known as the Southern Explorer Ridge, along with other smaller segments, such as the Northern Explorer Ridge. With a depth of , the Southern Explorer Ridge is relatively shallow in comparison with most other rift zones of the northeast Pacific Ocean, indicating there has been considerable volcanic activity along this part of the Explorer Ridge in the past 100,000 years. Magic Mountain (hydrothermal field), Magic Mountain, a large hydrothermal vent area on the Southern Explorer Ridge, is a scene of this volcanic activity. Unlike most hydrothermal systems found in the Pacific Ocean, the Magic Mountain site is situated outside the primary rift zone. The source for the hydrothermal fluid that fuels Magic Mountain probably rises along fracture systems associated with a recent episode of rifting that, in turn, followed a massive outpouring of lava. In contrast, the Northern Explorer Ridge has evolved into a complex compound structure consisting of several rift basins bounded by half-graben and arcuate shaped faults with a superimposed pattern of rhombohedral grabens and horst (geology), horsts.
The Explorer Ridge, an mid-ocean ridge, underwater mountain range lying west of Vancouver Island on the Coast of British Columbia, consists of a north-south trending rift zone. It contains one major segment known as the Southern Explorer Ridge, along with other smaller segments, such as the Northern Explorer Ridge. With a depth of , the Southern Explorer Ridge is relatively shallow in comparison with most other rift zones of the northeast Pacific Ocean, indicating there has been considerable volcanic activity along this part of the Explorer Ridge in the past 100,000 years. Magic Mountain (hydrothermal field), Magic Mountain, a large hydrothermal vent area on the Southern Explorer Ridge, is a scene of this volcanic activity. Unlike most hydrothermal systems found in the Pacific Ocean, the Magic Mountain site is situated outside the primary rift zone. The source for the hydrothermal fluid that fuels Magic Mountain probably rises along fracture systems associated with a recent episode of rifting that, in turn, followed a massive outpouring of lava. In contrast, the Northern Explorer Ridge has evolved into a complex compound structure consisting of several rift basins bounded by half-graben and arcuate shaped faults with a superimposed pattern of rhombohedral grabens and horst (geology), horsts.
 The Endeavour Segment, an active rift zone of the larger Juan de Fuca Ridge on the British Columbia Coast, contains a group of active black smokers called the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents, located southwest of Vancouver Island. This group of hydrothermal vents lies below sea level and consists of five hydrothermal fields, known as ''Sasquatch'', ''Saily Dawg'', ''High Rise'', ''Mothra'', and ''Main Endeavour''. Like typical hydrothermal vents, the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents form when cold seawater seeps into cracks and crevices in the Endeavour Segment where it becomes heated by magma that lies beneath the seafloor. As the water is heated, it rises and seeks a path back out into the Pacific Ocean through openings in the Endeavour Segment, forming hydrothermal vents. These hydrothermal vents release fluids with temperatures of over 300 °Celsius, C and have been a focus of research by Canadian and international scientists. The manned United States Navy deep-ocean research submersible DSV Alvin and the remotely operated underwater vehicle Jason (ROV), Jason have done work at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents. Joint Canada-United States studies have made use of the Canadian Remotely Operated Platform for Ocean Sciences. Fisheries and Oceans Canada has conducted extensive acoustic and mooredinstrument programs at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents since 1985.
The Endeavour Segment, an active rift zone of the larger Juan de Fuca Ridge on the British Columbia Coast, contains a group of active black smokers called the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents, located southwest of Vancouver Island. This group of hydrothermal vents lies below sea level and consists of five hydrothermal fields, known as ''Sasquatch'', ''Saily Dawg'', ''High Rise'', ''Mothra'', and ''Main Endeavour''. Like typical hydrothermal vents, the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents form when cold seawater seeps into cracks and crevices in the Endeavour Segment where it becomes heated by magma that lies beneath the seafloor. As the water is heated, it rises and seeks a path back out into the Pacific Ocean through openings in the Endeavour Segment, forming hydrothermal vents. These hydrothermal vents release fluids with temperatures of over 300 °Celsius, C and have been a focus of research by Canadian and international scientists. The manned United States Navy deep-ocean research submersible DSV Alvin and the remotely operated underwater vehicle Jason (ROV), Jason have done work at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents. Joint Canada-United States studies have made use of the Canadian Remotely Operated Platform for Ocean Sciences. Fisheries and Oceans Canada has conducted extensive acoustic and mooredinstrument programs at the Endeavour Hydrothermal Vents since 1985.
Northern Canada
 Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River southwest of Coronation Gulf in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive volcanic plateau, lava plateau and
Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River southwest of Coronation Gulf in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive volcanic plateau, lava plateau and large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
with an area of representing a volume of lavas of at least . With an area of and a volume of at least , it is larger than the Columbia River Basalt Group in the United States and comparable in size to the Deccan Traps in west-central India, making it one of the largest flood basalt events ever to appear on the North American continent, as well as on Earth. This massive eruptive event was associated with the Mackenzie magmatic event, that included the coeval, layered, mafic-ultramafic Muskox intrusion and the enormous Mackenzie dike swarm that diverges from the Coppermine River basalts, Coppermine River flood basalts. The maximum thickness of the flood basalts are and consist of 150 lava flows, each thick. These flood basalt lava flows were erupted during a single event that lasted less than five million years. Analysis of the chemical composition of the lavas gives important clues about the origin and dynamics of the flood basalt volcanism. The lowermost lavas were produced by melting in the garnet stability field below the surface at a depth of more than in a mantle plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hot ...
environment beneath the North American lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
. As the mantle plume intruded rocks of the Canadian Shield, it created an upwelling zone of molten rock known as the Mackenzie hotspot. Upper lavas were partly contaminated with crustal rocks as magmas from the mantle plume passed through the lower and upper crust.
During the Early Jurassic period 196 million years ago, the New England or Great Meteor hotspot existed in the Rankin Inlet area of southern Nunavut along the northwestern coast of Hudson Bay, producing kimberlite magmas. This marks the first appearance of the New England hotspot, as well as the oldest kimberlite eruption throughout the Great Meteor hotspot track, New England or Great Meteor hotspot track, which extends southeastwards across Canada and enters the northern Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
where the New England hotspot is located.
 The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province of northern Nunavut forms a large igneous province 95 to 92 million years old in the Canadian Arctic. Part of the larger High Arctic Large Igneous Province, it consists of two volcanic formations called the Ellesmere Island Volcanics and Strand Fiord Formation. In the Strand Fiord Formation, flood basalt lavas reach a thickness of at least . Flood basalts of the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province are similar to terrestrial flood basalts associated with breakup of continents, indicating the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province formed as a result of rifting of the Arctic Ocean and when the large underwater Alpha Ridge was still geologically active.
Widespread basalt volcanism occurred between 60.9 and 61.3 million years ago in the northern Labrador Sea, Davis Strait and in southern Baffin Bay on the eastern coast of Nunavut during the Paleocene period when North America and Greenland were being separated from tectonic movements. This resulted from
The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province of northern Nunavut forms a large igneous province 95 to 92 million years old in the Canadian Arctic. Part of the larger High Arctic Large Igneous Province, it consists of two volcanic formations called the Ellesmere Island Volcanics and Strand Fiord Formation. In the Strand Fiord Formation, flood basalt lavas reach a thickness of at least . Flood basalts of the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province are similar to terrestrial flood basalts associated with breakup of continents, indicating the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province formed as a result of rifting of the Arctic Ocean and when the large underwater Alpha Ridge was still geologically active.
Widespread basalt volcanism occurred between 60.9 and 61.3 million years ago in the northern Labrador Sea, Davis Strait and in southern Baffin Bay on the eastern coast of Nunavut during the Paleocene period when North America and Greenland were being separated from tectonic movements. This resulted from seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading or Seafloor spread is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
History of study
Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener an ...
where new oceanic crust, ocean seafloor was being created from rising magma. Scientific studies have indicated nearly 80% of the magma was erupted in one million years or less. The source for this volcanic activity was the Iceland plume along with its surface expression, the Iceland hotspot. This volcanic activity formed part of a large igneous province that is sunken beneath the northern Labrador Sea. Another period of volcanic activity began in the same region about 55 million years ago during the Eocene period when the north-south trending Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North Ame ...
began to form under the northern Atlantic Ocean east of Greenland. The cause of this volcanism might be related to partial melting from movement of a transform fault system extending from Labrador Sea to the south and Baffin Bay to the north. Although the region was carried away from the Iceland plume by going plate motion over millions of years, the source of the partial melting for the final period of volcanic activity may have been remnants of still anomalously hot Iceland plume magma which were left stranded beneath the North American lithosphere in the Paleocene period. Most diatreme
A diatreme, sometimes known as a maar-diatreme volcano, is a volcanic pipe formed by a gaseous explosion. When magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the ...
s in the Northwest Territories were formed by volcanic eruptions between 45 and 75 million years ago during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
and Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
periods.
More recent volcanic activity has created a northwest trending line of volcanic rocks called the Wrangell Volcanic Belt. This volcanic belt lies largely in the U.S. state of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
, but extends across the Alaska-Yukon border into southwestern Yukon where it contains scattered remnants of subaerial lavas and pyroclastic rocks which are preserved along the entire eastern fringe of the ice covered Saint Elias Mountains. The Wrangell Volcanic Belt formed as a result of arc volcanism related to subduction of the Pacific Plate under the northern portion of the North American Plate. Over large areas extrusive rocks lie in flat undisturbed piles on a Tertiary surface of moderate relief. Locally, however, strata of the same age have been affected by a late pulse of tectonism, during which they were faulted, contorted into tight symmetrical folds, or overridden by pre-Tertiary basement rocks along southwesterly dipping thrust faults. Considerable recent uplift, accompanied by rapid erosion, has reduced once vast areas of upper Tertiary volcanic rocks to small isolated remnants. Although no eruptions have occurred in the Yukon portion of the Wrangell Belt for the past five million years, two large (Volcanic Explosivity Index, VEI-6) explosive eruptions from Mount Churchill west of the Alaska-Yukon border, created the White River Ash deposit. This volcanic ash deposit is estimated 1,890 and 1,250 years old, covering more than of northwestern Canada and adjacent eastern Alaska. Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American legends about the area indicate the final eruption from Mount Churchill 1,250 years ago disrupted food supplies and forced them to move further south.
The Yukon portion of the northwest trending Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province includes the youngest volcanoes in Northern Canada. The Fort Selkirk Volcanic Field in central Yukon consists of valley-filling basalt lava flows and cinder cones. Ne Ch'e Ddhawa, a cinder cone away from the connection of the Yukon River, Yukon and Pelly River, Pelly rivers formed between 0.8 and one million years ago when this area lied beneath the vast Cordilleran Ice Sheet. The youngest volcano, Volcano Mountain just north of the junction of the Yukon and Pelly rivers, formed in past 10,000 years (Holocene), producing lava flows that remain unvegetated and appear to be only a few hundred years old. However, dating of sediments in a lake impounded by the lava flows indicated that the youngest lava flows could not be younger than mid-Holocene and could be early Holocene or older. Therefore, the most recent activity in the Fort Selkirk volcanic field is unknown. The lava flows from Volcano Mountain are unusual because they originate much deeper in the Earth's mantle (geology), mantle than the more common basaltic lava flows found throughout the Yukon and are very uncommon in the geological record. This lava, known as olivine nephelinite, is also unusual because it contains small, angular to rounded fragments of rock called nodule (geology), nodules.
Economic geology
Greenstone belts
 The predominantly volcanic Archean and Proterozoic
The predominantly volcanic Archean and Proterozoic greenstone belt
Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary rocks that occur within Archaean and Proterozoic cratons between granite and gneiss bodies.
The name comes from the green ...
s throughout Canada are important for estimating Canada's mineral potential. Consequently, geologists study greenstone belts to understand the volcanoes and the environment in which they erupted, and to provide a working model for mineral exploration. The 1,904‑ to 1,864‑million-year-old Flin Flon greenstone belt
The Flin Flon greenstone belt, also referred to as the Flin Flon – Snow Lake greenstone belt, is a Precambrian greenstone belt located in the central area of Manitoba and east-central Saskatchewan, Canada (near Flin Flon). It lies in the central ...
of central Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
and east-central Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
is one of the largest Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions (eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ...
age volcanogenic massive sulfide ore deposits in the world, containing 27 copper-zinc-(gold) deposits from which more than 183 million tonnes of sulfide ore have been mined. The 2,575‑million-year-old Yellowknife greenstone belt in the Northwest Territories is the host for world-class gold deposits with total production of 15 million ounces of gold. In the Archean Hope Bay greenstone belt of western Nunavut, three large gold deposits have been known as Doris, Boston and Madrid, while the 2,677‑million-year-old Abitibi greenstone belt
The Abitibi greenstone belt is a 2,800-to-2,600-million-year-old greenstone belt that spans across the Ontario–Quebec border in Canada. It is mostly made of volcanic rocks, but also includes ultramafic rocks, mafic intrusions, granitoid rocks, ...
of Ontario and Quebec is the second most prolific gold producing area on Earth; the most prolific gold producing area is the Witwatersrand hill range in South Africa.

Intrusions
Other magmatic formations, such asdike swarm
A dike swarm (American spelling) or dyke swarm (British spelling) is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes ...
s and sill (geology), sills, are known to contain base and precious metal deposits. The 2,500- to 2,450-million-year-old Matachewan dike swarm of eastern Ontario hosts the 2,491- to 2,475-million-year-old long East Bull Lake Intrusion and associated intrusions. The 2,217- to 2,210-million-year-old Ungava magmatic event was the source for the Nipissing sills of Ontario and have been historically important for copper, silver, and arsenic mineralization, and also have the potential to contain platinum group metals. A third major event is the 1,885‑ to 1,865‑million-year-old magmatism of the Circum-Superior Belt
The Circum-Superior Belt is a widespread Paleoproterozoic large igneous province in the Canadian Shield of Northern, Western and Eastern Canada. It extends more than from northeastern Manitoba through northwestern Ontario, southern Nunavut to ...
surrounding much of the Superior craton from the Labrador Trough
The Labrador Trough or the New Quebec Orogen is a long and wide geologic belt in Canada, extending south-southeast from Ungava Bay through Quebec and Labrador.
The trough is a linear belt of sedimentary and volcanic rocks which developed in an ...
in Labrador and northeastern Quebec, though the Cape Smith Belt The Cape Smith Belt is an early Proterozoic thrust belt in northern Quebec, Canada.
References
Geology of Quebec
{{Canada-geology-stub ...
in northern Quebec, the Belcher Islands
The Belcher Islands ( iu, script=latn, ᓴᓪᓚᔪᒐᐃᑦ, Sanikiluaq) are an archipelago in the southeast part of Hudson Bay near the centre of the Nastapoka arc. The Belcher Islands are spread out over almost . Administratively, they belon ...
in southern Nunavut, the Fox River and Thompson
Thompson may refer to:
People
* Thompson (surname)
* Thompson M. Scoon (1888–1953), New York politician
Places Australia
*Thompson Beach, South Australia, a locality
Bulgaria
* Thompson, Bulgaria, a village in Sofia Province
Canada
* ...
belts in northern Manitoba, the Winnipegosis komatiite belt
The Winnipegosis komatiite belt is a long and wide greenstone belt located in the Lake Winnipegosis area of central Manitoba, Canada. It has no surface exposure and was identified based on geophysical signatures and drilling during mineral explo ...
in central Manitoba, and on the southern side of the Superior craton
The Superior Craton is a stable crustal block covering Quebec, Ontario, and southeast Manitoba in Canada, and northern Minnesota in the United States. It is the biggest craton among those formed during the Archean period. A craton is a large part ...
in the Animikie Basin of northwestern Ontario. Included within the Circum-Superior large igneous province are major nickel deposits of the Thompson and Raglan belts, which were likely derived from more than one magma source. The major 1,267‑million-year-old Mackenzie dike swarm magmatism in the western part of the Canadian Shield is the host for the highly prospected Muskox intrusion. Another significant event was the magmatism that formed the 723‑million-year-old Franklin dike swarm of Northern Canada and has been heavily mined for nickel, copper, and platinum group metals. The 230‑million-year-old accreted oceanic plateau, Wrangellia in British Columbia and Yukon, has also been searched for nickel, copper, and platinum group metals.
Diatremes
 The kimberlite
The kimberlite diatreme
A diatreme, sometimes known as a maar-diatreme volcano, is a volcanic pipe formed by a gaseous explosion. When magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the ...
s, or pipes, across Canada have also been important economically, because kimberlite magmas are the world's main source of gem-quality diamonds. Kimberlite pipes form when kimberlite magmas rise considerably from depths as great as . As the kimberlite magmas approach a depth of at least , the magma explodes violently through the Earth's crust, carrying fragments of rock that it has collected along the way and, in the right conditions, possibly diamonds, to the surface. The Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
(ca. 55–50 Ma) age diatremes of the Lac de Gras kimberlite field in the central Slave craton of the Northwest Territories support two world-class diamond mines, called Ekati Diamond Mine, Ekati and Diavik Diamond Mine, Diavik. Ekati, Canada's first diamond mine, has produced of diamonds out of six open-pit mining, open pits between 1998 and 2008, while Diavik, to the southeast, has produced of diamonds since its foundation in 2003. The diamondiferous Drybones Bay kimberlite pipe is the largest diatreme discovered in the Northwest Territories, measuring . Diamondiferous diatremes throughout the Northwest Territories and Alberta have the potential to make Canada one of the world's major producers of gem-quality diamonds.
Recent activity
Canada continues to be volcanically active, but the dispersed population has witnessed few eruptions due to the remoteness of the volcanoes and their low level of activity. The span of recorded and witnessed volcanic activity in Canada differs from region to region and at least two eruptions have been witnessed by people. Part of thePacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions and ...
, more than 200 potentially active volcanoes exist throughout Canada, 49 of which have erupted in the past 10,000 years (Holocene). This is very recent in geological terms, suggesting volcanoes in Canada have ongoing activity. Ongoing scientific studies have indicated there have been earthquakes associated with at least ten Canadian volcanoes, including: Mount Garibaldi, Hoodoo Mountain, Castle Rock (volcano), Castle Rock, Mount Cayley, The Volcano (British Columbia), The Volcano, Crow Lagoon, Silverthrone Caldera, Mount Meager massif, the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, and the Mount Edziza volcanic complex.

 The Mount Meager massif in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt of southwestern British Columbia was the source for a massive (Volcanic Explosivity Index, VEI-5) Plinian eruption 2,350 years ago similar in character to the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the U.S. state of Washington (U.S. state), Washington. The eruption originated from a vent on the northeast flank of Plinth Peak, the highest and one of four overlapping stratovolcanoes which together form the Mount Meager massif. This activity produced a diverse sequence of volcanic deposits, well exposed in Hill, bluffs along the long Lillooet River, which are grouped as part of the Pebble Creek Formation. The explosive power associated with this Plinian eruption sent an eruption column, ash column estimated to have risen at least above Meager, indicating it entered stratosphere, the second major layer of the Earth's atmosphere. As prevailing winds sent ash and dust as far as to the east, it created the large Bridge River Ash deposit, extending from Mount Meager to central Alberta. Pyroclastic flows travelled downstream from the vent and buried trees along Meager's forested slopes, which were burned in place. An unusual, thick apron of welded Vitrophyre, vitrophyric breccia may represent the explosive collapse of a former
The Mount Meager massif in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt of southwestern British Columbia was the source for a massive (Volcanic Explosivity Index, VEI-5) Plinian eruption 2,350 years ago similar in character to the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the U.S. state of Washington (U.S. state), Washington. The eruption originated from a vent on the northeast flank of Plinth Peak, the highest and one of four overlapping stratovolcanoes which together form the Mount Meager massif. This activity produced a diverse sequence of volcanic deposits, well exposed in Hill, bluffs along the long Lillooet River, which are grouped as part of the Pebble Creek Formation. The explosive power associated with this Plinian eruption sent an eruption column, ash column estimated to have risen at least above Meager, indicating it entered stratosphere, the second major layer of the Earth's atmosphere. As prevailing winds sent ash and dust as far as to the east, it created the large Bridge River Ash deposit, extending from Mount Meager to central Alberta. Pyroclastic flows travelled downstream from the vent and buried trees along Meager's forested slopes, which were burned in place. An unusual, thick apron of welded Vitrophyre, vitrophyric breccia may represent the explosive collapse of a former lava dome
In volcanology, a lava dome is a circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano. Dome-building eruptions are common, particularly in convergent plate boundary settings. Around 6% of eruptions on ...
which deposited ash several meters in thickness near the vent area. This collapse blocked the Lillooet River to a height of at least , forming a lake. The lake reached a maximum elevation of and thus was at least deep. The pyroclastic deposits blocking the Lillooet River eventually eroded from water activity, causing a massive outburst flood that sent small house-sized boulders down the Lillooet River valley, and formed high Keyhole Falls. The final phase of activity produced a long glassy dacite lava flow that varies from thick. This is the largest known explosive eruption in Canada in the past 10,000 years. Two clusters of hot springs are found at the Mount Meager massif, suggesting magmatic heat is still present and volcanic activity continues.
 The massive Mount Edziza volcanic complex in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northern British Columbia has had more than 20 eruptions throughout the past 10,000 years (Holocene), including Mess Lake Cone, Kana Cone, Cinder Cliff, Icefall Cone, Ridge Cone, Williams Cone, Walkout Creek Cone, Moraine Cone, Sidas Cone, Sleet Cone, Storm Cone, Triplex Cone, Twin Cone, Cache Hill, Camp Hill (British Columbia), Camp Hill, Cocoa Crater, Coffee Crater, Nahta Cone, Tennena Cone, The Saucer, and the well-preserved Eve Cone. Active or recently active hot springs are found in several areas along the western flank of Edziza's lava plateau, including Elwyn springs (36 degree (temperature), °Celsius, C), Taweh springs (46 °C), and inactive springs near Mess Lake. All three hydrothermal areas are near the youngest lava fields on the lava plateau and are probably associated with the most recent volcanic activity at the Mount Edziza volcanic complex. An undated pumice deposit exists throughout the complex estimated to be younger than 500 years.
The massive Mount Edziza volcanic complex in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province of northern British Columbia has had more than 20 eruptions throughout the past 10,000 years (Holocene), including Mess Lake Cone, Kana Cone, Cinder Cliff, Icefall Cone, Ridge Cone, Williams Cone, Walkout Creek Cone, Moraine Cone, Sidas Cone, Sleet Cone, Storm Cone, Triplex Cone, Twin Cone, Cache Hill, Camp Hill (British Columbia), Camp Hill, Cocoa Crater, Coffee Crater, Nahta Cone, Tennena Cone, The Saucer, and the well-preserved Eve Cone. Active or recently active hot springs are found in several areas along the western flank of Edziza's lava plateau, including Elwyn springs (36 degree (temperature), °Celsius, C), Taweh springs (46 °C), and inactive springs near Mess Lake. All three hydrothermal areas are near the youngest lava fields on the lava plateau and are probably associated with the most recent volcanic activity at the Mount Edziza volcanic complex. An undated pumice deposit exists throughout the complex estimated to be younger than 500 years.
 Kostal Cone in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field of east-central British Columbia is a cinder cone responsible for basaltic lava flows comprising a lava bed, damming the southern end of McDougall Lake. There has been activity at this site as recently as 7,600 years ago at Dragon Cone, though more likely less than 1,000 years ago. Kostal Cone is too young for the potassium-argon dating technique (usable on specimens over 100,000 years old), and no charred organic material for radiocarbon dating has been found. However, the uneroded structure of the cone with the existence of trees on its flanks and summit have made it an area for dendrochronology studies, which reveals the growth of tree-ring patterns. Tree-ring dating has revealed an age of about 400 years for Kostal Cone, indicating it formed around 1500. This makes Kostal Cone the youngest volcano in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and thus one of the youngest in Canada.
Kostal Cone in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field of east-central British Columbia is a cinder cone responsible for basaltic lava flows comprising a lava bed, damming the southern end of McDougall Lake. There has been activity at this site as recently as 7,600 years ago at Dragon Cone, though more likely less than 1,000 years ago. Kostal Cone is too young for the potassium-argon dating technique (usable on specimens over 100,000 years old), and no charred organic material for radiocarbon dating has been found. However, the uneroded structure of the cone with the existence of trees on its flanks and summit have made it an area for dendrochronology studies, which reveals the growth of tree-ring patterns. Tree-ring dating has revealed an age of about 400 years for Kostal Cone, indicating it formed around 1500. This makes Kostal Cone the youngest volcano in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and thus one of the youngest in Canada.
 Tseax Cone, a young cinder cone at the southernmost end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, was the source for a major basalt lava flow eruption around the years 1750 and 1775 that travelled into the Tseax River, damming it and forming Lava Lake (British Columbia), Lava Lake. The lava flow subsequently travelled north to the Nass River, where it filled the flat valley floor for an additional , making the entire lava flow long. Native legends from Nisga'a people in the area tell of a prolonged period of disruption by the volcano, including the destruction of two Nisga'a villages known as Lax Ksiluux, British Columbia, Lax Ksiluux and Wii Lax K'abit. Nisga'a people dug pits for shelter but at least 2,000 Nisga'a people were killed due to volcanic gases and poisonous smoke (most likely carbon dioxide). This is Canada's worst known geophysical disaster. It is the only eruption in Canada for which legends of First Nations in Canada, First Nations people have been proven true. As of 1993, the Tseax Cone quietly rests in Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park.
Tseax Cone, a young cinder cone at the southernmost end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, was the source for a major basalt lava flow eruption around the years 1750 and 1775 that travelled into the Tseax River, damming it and forming Lava Lake (British Columbia), Lava Lake. The lava flow subsequently travelled north to the Nass River, where it filled the flat valley floor for an additional , making the entire lava flow long. Native legends from Nisga'a people in the area tell of a prolonged period of disruption by the volcano, including the destruction of two Nisga'a villages known as Lax Ksiluux, British Columbia, Lax Ksiluux and Wii Lax K'abit. Nisga'a people dug pits for shelter but at least 2,000 Nisga'a people were killed due to volcanic gases and poisonous smoke (most likely carbon dioxide). This is Canada's worst known geophysical disaster. It is the only eruption in Canada for which legends of First Nations in Canada, First Nations people have been proven true. As of 1993, the Tseax Cone quietly rests in Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park.
 An eruption was reported by placer mining, placer miners on November 8, 1898 in the Atlin Volcanic Field of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province adjacent to Ruby Mountain volcano south of Gladys Lake when volcanic ash was said to be falling for many days. During the eruption the adjacent placer miners were able to work at nights due to incandescent glow from the eruption. A news report published on December 1, 1898 by the American newspaper publisher The New York Times stated: ''Kinslee and T. P. James, Denver mining men who with Col. Hughes of Rossland have just returned from Alaska, report that a volcano is in active eruption about fifty miles from Atlin City. No name has yet been given to the volcano, but the officials of Atlin are preparing for a trip of inspection and will christen it. It is said to be the second in a string of four mountains lying fifty miles due south of Lake Gladys, all of which are more than 1,400 feet high.'' In 1898 the Atlin, British Columbia, Atlin area was in Alaska boundary dispute, dispute with the Alaska-British Columbia boundary, leading American news broadcasters stating the Atlin area was in Alaska rather than in northwestern British Columbia. This Alaska-British Columbia boundary dispute was eventually resolved by arbitration in 1903 and no evidence for the 1898 eruption has been found, leading researchers to speculate about the eruption and report it as uncertain.
An eruption was reported by placer mining, placer miners on November 8, 1898 in the Atlin Volcanic Field of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province adjacent to Ruby Mountain volcano south of Gladys Lake when volcanic ash was said to be falling for many days. During the eruption the adjacent placer miners were able to work at nights due to incandescent glow from the eruption. A news report published on December 1, 1898 by the American newspaper publisher The New York Times stated: ''Kinslee and T. P. James, Denver mining men who with Col. Hughes of Rossland have just returned from Alaska, report that a volcano is in active eruption about fifty miles from Atlin City. No name has yet been given to the volcano, but the officials of Atlin are preparing for a trip of inspection and will christen it. It is said to be the second in a string of four mountains lying fifty miles due south of Lake Gladys, all of which are more than 1,400 feet high.'' In 1898 the Atlin, British Columbia, Atlin area was in Alaska boundary dispute, dispute with the Alaska-British Columbia boundary, leading American news broadcasters stating the Atlin area was in Alaska rather than in northwestern British Columbia. This Alaska-British Columbia boundary dispute was eventually resolved by arbitration in 1903 and no evidence for the 1898 eruption has been found, leading researchers to speculate about the eruption and report it as uncertain.
 The Volcano (British Columbia), The Volcano at the southern end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province just north of the Alaska-British Columbia boundary is probably the youngest in Canada. It is a poorly built cinder cone made of loose volcanic ash, lapilli-sized tephra and volcanic bombs. Lying above a remote mountain ridge in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it is responsible for lava flow eruptions in 1904 and older that traveled south through river valleys where they crossed the border into the U.S. state of Alaska and dammed the Blue River, a short tributary of the Unuk River. In doing so it formed several small lakes. This eruption had a massive effect on fish, plant and animal inhabitants of the valley, but there is no record of its impact on people, most likely because people were not in the remote area. The entire length of the lava flows are at least and still contain the original lava features from when they were erupted, including pressure ridge (lava), pressure ridges and lava channels. However, sections of the lava flows have collapsed into underlying lava tubes to form cavities. Tephra and scoria from The Volcano covers adjacent mountain ridges and even through it is very young, it has been reduced by erosion from alpine glacial ice found in the heavily glaciated Coast Mountains. The estimated volume of lava and ash from The Volcano is .
The Volcano (British Columbia), The Volcano at the southern end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province just north of the Alaska-British Columbia boundary is probably the youngest in Canada. It is a poorly built cinder cone made of loose volcanic ash, lapilli-sized tephra and volcanic bombs. Lying above a remote mountain ridge in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it is responsible for lava flow eruptions in 1904 and older that traveled south through river valleys where they crossed the border into the U.S. state of Alaska and dammed the Blue River, a short tributary of the Unuk River. In doing so it formed several small lakes. This eruption had a massive effect on fish, plant and animal inhabitants of the valley, but there is no record of its impact on people, most likely because people were not in the remote area. The entire length of the lava flows are at least and still contain the original lava features from when they were erupted, including pressure ridge (lava), pressure ridges and lava channels. However, sections of the lava flows have collapsed into underlying lava tubes to form cavities. Tephra and scoria from The Volcano covers adjacent mountain ridges and even through it is very young, it has been reduced by erosion from alpine glacial ice found in the heavily glaciated Coast Mountains. The estimated volume of lava and ash from The Volcano is .
 A series of 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes, earthquakes of less than magnitude 3.0 were recorded by seismographs in the Baezaeko River region west of Nazko Cone in the Anahim Volcanic Belt on October 9, 2007. The cause of these earthquakes was magma intruding into rock below the surface. Since then more than 1,000 small earthquakes have been recorded. Because of the small size of the earthquake swarms, Natural Resources Canada has added more seismographs in the region for better location and depth accuracy. However, the size and number of the 2007 earthquake swarms indicate there is currently no threat of an eruption. Before magma could erupt in the area adjacent to Nazko Cone, it is expected the size and number of the earthquakes would rise considerably, presaging an eruption.
A series of 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes, earthquakes of less than magnitude 3.0 were recorded by seismographs in the Baezaeko River region west of Nazko Cone in the Anahim Volcanic Belt on October 9, 2007. The cause of these earthquakes was magma intruding into rock below the surface. Since then more than 1,000 small earthquakes have been recorded. Because of the small size of the earthquake swarms, Natural Resources Canada has added more seismographs in the region for better location and depth accuracy. However, the size and number of the 2007 earthquake swarms indicate there is currently no threat of an eruption. Before magma could erupt in the area adjacent to Nazko Cone, it is expected the size and number of the earthquakes would rise considerably, presaging an eruption.
Mitigation and vulnerability
 In Canada, even though volcanoes pose significant threats to local communities and any sizable eruption would affect Canada's economy, the work of understanding the frequency and eruption characteristics at volcanoes in Canada is a slow process. This is because most of Canada's dormant and potentially active volcanoes are located in isolated jagged regions, very few scientists study Canadian volcanoes and the provision of money in the Canadian government is limited. Because of these issues, scientists studying Canada's volcanoes have a basic understanding of Canada's volcanic heritage and how it might impact people in the future. Volcanologists are aware that certain areas in Canada have higher levels of volcanic activity than others and how eruptions in these areas might affect people and the environment they live in. When a volcano is showing evidence of volcanic activity, quick action will be required to better understand the process. The lowest possibility for an eruption in Canada per year is approximately 1/200; for a passive lava eruption the possibility is about 1/220, and for a major explosive eruption it is about 1/3333. Even though volcanoes do not seem to be part of the everyday reality of Canadians, recurrent earthquakes and the formation of large
In Canada, even though volcanoes pose significant threats to local communities and any sizable eruption would affect Canada's economy, the work of understanding the frequency and eruption characteristics at volcanoes in Canada is a slow process. This is because most of Canada's dormant and potentially active volcanoes are located in isolated jagged regions, very few scientists study Canadian volcanoes and the provision of money in the Canadian government is limited. Because of these issues, scientists studying Canada's volcanoes have a basic understanding of Canada's volcanic heritage and how it might impact people in the future. Volcanologists are aware that certain areas in Canada have higher levels of volcanic activity than others and how eruptions in these areas might affect people and the environment they live in. When a volcano is showing evidence of volcanic activity, quick action will be required to better understand the process. The lowest possibility for an eruption in Canada per year is approximately 1/200; for a passive lava eruption the possibility is about 1/220, and for a major explosive eruption it is about 1/3333. Even though volcanoes do not seem to be part of the everyday reality of Canadians, recurrent earthquakes and the formation of large mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arise ...
s in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
indicate this part of Canada is still geologically active. The possibility of an eruption, even a large explosive one, cannot be ruled out. Quiet as they currently seem, volcanoes in Northern and Western Canada are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions and ...
. Along with volcanoes associated with recent earthquake activity, a scenario of an eruption at Mount Cayley in southwestern British Columbia illustrates how Western Canada is in danger to a volcanic eruption, which has not erupted for at least 310,000 years. This impact is becoming even more likely as population in the Pacific Northwest increases and development spreads. The scenario is based on former eruptions in the north-south trending Garibaldi Volcanic Belt and includes both explosive and passive eruptions. Its effect is mostly due to the attention of defenseless public services in canyons. However, the threat from volcanoes outside of Canada seems much greater than the threat from volcanoes within Canada because of the lack of monitoring data at Canadian volcanoes and the age of most volcanoes in Canada is poorly known. But for some, their minimal degree of erosion indicates they formed much less than 10,000 years ago, including the Milbanke Sound Group on Price Island (British Columbia), Price Island, Dufferin Island, Swindle Island, Lake Island (British Columbia), Lake Island, and Lady Douglas Island in the Milbanke Sound area of coastal British Columbia. However, it is known volcanoes in the U.S. states of Alaska, Washington (U.S. state), Washington, Oregon and California have been more active in historic times than those within Canada. Therefore, volcanoes in the United States are monitored with caution and attention by the United States Geological Survey.
 Growing awareness of volcanism, especially the threat from volcanoes in the United States, has led to a number of changes in the way Canadians are dealing with volcanic hazards. For example, The Barrier, an unstable volcanic dam, lava dam retaining the Garibaldi Lake system of southwestern British Columbia, has in the past unleashed several debris flows, most recently in 1855–1856. This led to the evacuation of the small resort village of Garibaldi, British Columbia, Garibaldi nearby and the relocation of residents to new recreational subdivisions away from the hazard zone. Should The Barrier completely collapse, Garibaldi Lake would be entirely released and downstream damage in the Cheakamus River, Cheakamus and Squamish River, Squamish rivers would be considerable, including major damage to the town of Squamish, British Columbia, Squamish and possibly an impact-wave on the waters of Howe Sound that would reach Vancouver Island. The Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan, Canada's volcanic emergency notification program, was established to outline the notification procedure of some of the main agencies that would be involved in response to a volcanic eruption in Canada, an eruption close to Canada's borders, or an eruption significant enough to have an effect on Canada and its people. It focuses primarily on aviation safety because jet aircraft can quickly enter areas of volcanic ash. The program notifies all impacted agencies that have to deal with volcanic events. Aircraft are rerouted away from hazardous ash and people on the ground are notified of potential ash fall.
Growing awareness of volcanism, especially the threat from volcanoes in the United States, has led to a number of changes in the way Canadians are dealing with volcanic hazards. For example, The Barrier, an unstable volcanic dam, lava dam retaining the Garibaldi Lake system of southwestern British Columbia, has in the past unleashed several debris flows, most recently in 1855–1856. This led to the evacuation of the small resort village of Garibaldi, British Columbia, Garibaldi nearby and the relocation of residents to new recreational subdivisions away from the hazard zone. Should The Barrier completely collapse, Garibaldi Lake would be entirely released and downstream damage in the Cheakamus River, Cheakamus and Squamish River, Squamish rivers would be considerable, including major damage to the town of Squamish, British Columbia, Squamish and possibly an impact-wave on the waters of Howe Sound that would reach Vancouver Island. The Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan, Canada's volcanic emergency notification program, was established to outline the notification procedure of some of the main agencies that would be involved in response to a volcanic eruption in Canada, an eruption close to Canada's borders, or an eruption significant enough to have an effect on Canada and its people. It focuses primarily on aviation safety because jet aircraft can quickly enter areas of volcanic ash. The program notifies all impacted agencies that have to deal with volcanic events. Aircraft are rerouted away from hazardous ash and people on the ground are notified of potential ash fall.
Monitoring
Currently no volcanoes in Canada are monitored closely enough by the Geological Survey of Canada to ascertain how active their magma chambers are. An existing network of seismometer, seismographs has been established to monitor tectonic earthquakes and is too far away to provide a good indication of what is happening beneath them. It may sense an increase in activity if a volcano becomes very restless, but this may only provide a warning for a large eruption. It might detect activity only once a volcano has started erupting.See also
* List of volcanoes in Canada * Geography of CanadaReferences
External links
Catalogue of Canadian volcanoes
Global Volcanism Program: Volcanoes of Canada and the western USA
GVP: Volcanoes of Canada
Erica A. Massey: A Comparative Study of Glaciovolcanic Palagonitization of Tholeitic and Alkaline Sideromelane in Helgafell, Icland, and Wells Gray-Clearwater Volcanic Filed, BC, Canada. B.Sc., The University of British Columbia, 2014
{{DEFAULTSORT:Volcanism Of Canada Volcanism of Canada, Geographic areas of seismological interest Natural history of Canada Natural hazards in Canada